Table of Contents
One of the common questions in bitcoin that often perplex people is about the origins of bitcoins: How are bitcoins created? To fully appreciate the innovative nature of Bitcoin, it’s essential to understand its creation process.
The term “mining” frequently used in this context can lead to confusion, as bitcoin don’t exist in a physical form as one might assume from the mining analogy. Instead, bitcoin are units of the digital currency, each uniquely associated with public keys and recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
How Are Bitcoins Created?
Let’s delve deeper into the concept of mining and how it fundamentally differs from traditional mining practices to better understand where the bitcoin we interact with comes from.
Raw hex version of Bitcoin’s Genesis Block, the first block ever mined on the Bitcoin Network
What Exactly is Bitcoin Mining?
Contrary to the traditional concept of mining, where physical resources like ore or precious metals are extracted, Bitcoin mining involves solving complex cryptographic problems using computational power. In traditional mining, considerable effort is put into locating and extracting physical resources. In contrast, Bitcoin mining requires computational power to solve cryptographic puzzles.

Coal mining in an open pit
Bitcoin miners are given a range of potential solutions to validate a new block of Bitcoin transactions. The challenge lies in finding the missing part of the cryptographic equation, known as the hash, that falls within this range. This process is competitive; the first miner to discover the hash is rewarded with new bitcoin.
To visualize this, imagine being given a 9×9 sudoku puzzle with some numbers already in place. Your goal is to complete the puzzle before anyone else. In Bitcoin mining, this puzzle is akin to finding the right hash value in a sea of quadrillions of possibilities, far more complex than the sudoku analogy suggests.
The Purpose of Bitcoin Mining
Why invest significant time and resources in solving these complex puzzles? Like traditional miners who are rewarded with ore or currency, Bitcoin miners receive new bitcoin as rewards. For each block of transactions solved, miners are currently rewarded with 6.25 bitcoins, known as the block reward or subsidy. This amount, however, is set to decrease with future halvings.
Mining is not solely about earning bitcoin; it’s a critical process for verifying new transactions and adding them to the blockchain, thus maintaining the network’s integrity and security.
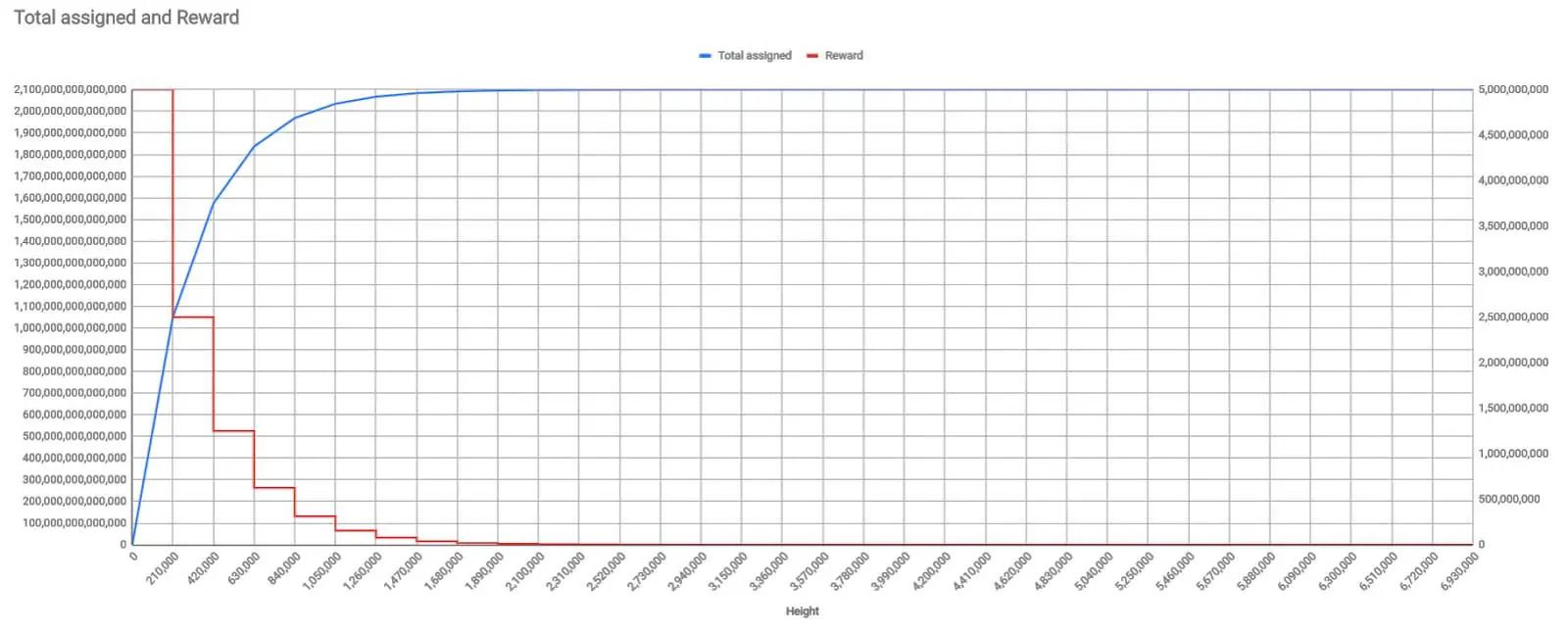
The Bitcoin supply vs reward curve schedule
The Role of the Bitcoin Protocol in Mining
The process of mining and the rewards associated with it are governed by the Bitcoin Protocol. These rules are crucial in defining the operational framework of Bitcoin mining and the overall management of the Bitcoin network. Let’s explore the key elements of the Bitcoin Protocol that directly impact the mining process.
Supply Emission: The protocol dictates how new bitcoin are introduced. The mining reward halves every 210,000 blocks, approximately every four years, in an event known as “halving.”
Supply Cap: There is a finite limit of 21 million bitcoins, making Bitcoin a scarce resource.
Difficulty Adjustment: The protocol ensures that it takes an average of 10 minutes to solve a block. The difficulty of solving these cryptographic puzzles is adjusted every 2,016 blocks, based on the total computing power in the network.
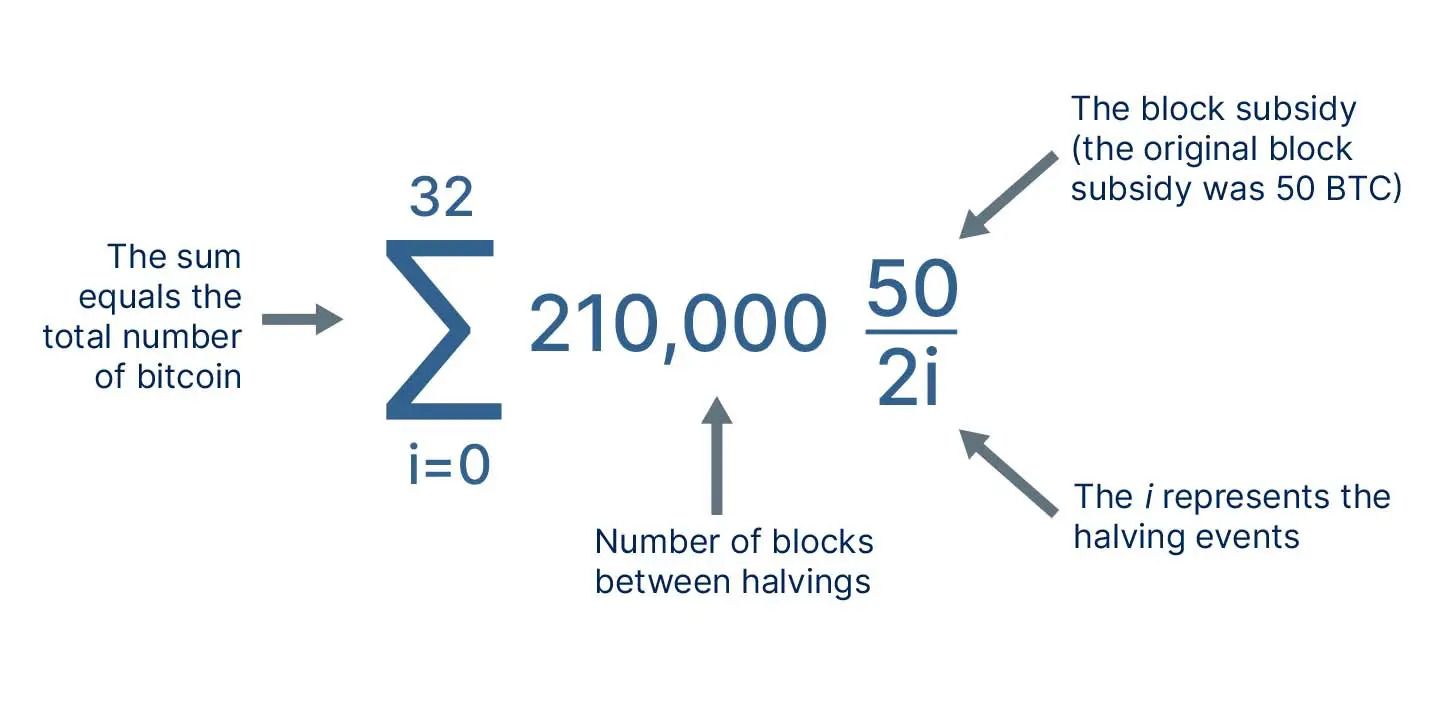
Bitcoin mining formula
The Global Competition and Scaling Difficulty
Bitcoin mining is a global competition, where the complexity of the puzzles scales with the computational power dedicated. This dynamic scaling ensures that, on average, a new block is solved every ten minutes, irrespective of the total computational power in the network. This adjustment is crucial for maintaining the network’s efficiency and the regular creation of new bitcoin.
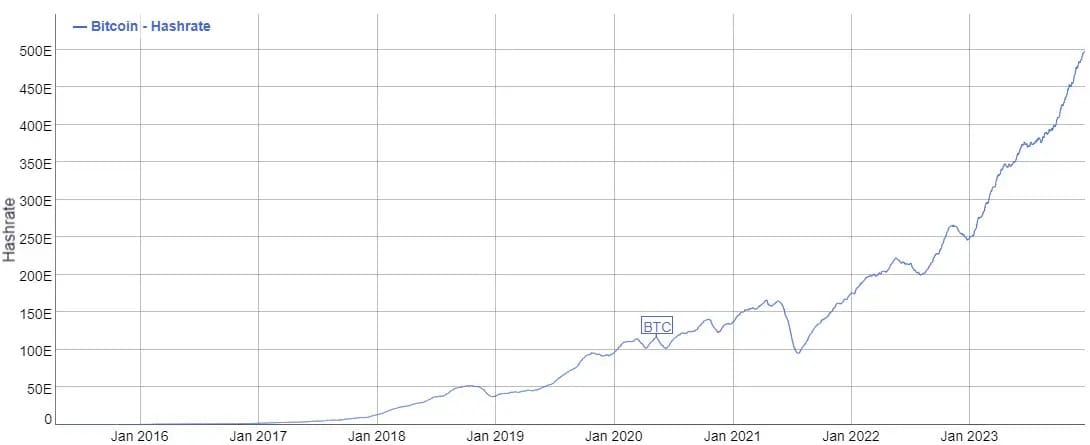
Bitcoin hashrate historical chart — Source: BitInfoCharts
Enhanced Security and Decentralization Through Mining
An often overlooked yet crucial aspect of Bitcoin mining is its role in enhancing the security and decentralization of the network.
Each miner’s effort contributes to a more robust and secure system. By solving cryptographic puzzles and validating transactions, miners help prevent double-spending, a potential issue where the same bitcoin is spent more than once. Ensuring this takes considerable investment into equipment and electricity.
The block reward not only adds new bitcoin to the total supply according to the protocol rules, but also incentivizes the investment into securing the network.
Conclusion
Understanding Bitcoin supply increase through mining is crucial for comprehending its underlying value and functionality. While complex, this process ensures the security, integrity, and decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network. As Bitcoin continues to grow in popularity and use, the role of mining as a foundational element of this digital asset remains a fascinating and essential topic for enthusiasts, investors, and skeptics alike.
FAQ
How are bitcoins created?
Bitcoins are created through a process called mining, which involves solving complex cryptographic problems using computational power.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of solving cryptographic puzzles using computational power to validate new blocks of Bitcoin transactions. Miners compete to find the correct hash value to add a new block to the blockchain.
How does Bitcoin mining differ from traditional mining practices?
Unlike traditional mining that extracts physical resources, Bitcoin mining involves solving cryptographic puzzles, and miners are rewarded with new bitcoins for their efforts.
Why do miners invest time and resources in Bitcoin mining?
Miners invest in Bitcoin mining to earn new bitcoins as rewards. Additionally, mining plays a crucial role in verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain, maintaining the network’s integrity and security.
What are the rules of Bitcoin mining?
The Bitcoin Protocol governs the rules of mining, including supply emission, supply cap, and difficulty adjustment. These rules define the operational framework and management of the Bitcoin network.
How often does the Bitcoin mining reward halve, and why?
The mining reward halves approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks, in an event known as u0022halving.u0022 This is dictated by the Bitcoin Protocol.
How many bitcoins will ever exist?
There is a finite limit of 21 million bitcoins, making Bitcoin a scarce resource according to the rules set by the Bitcoin Protocol.
What is difficulty in Bitcoin mining?
The Bitcoin Protocol includes difficulty adjustment, which ensures that, on average, it takes 10 minutes to solve a block. The difficulty is adjusted every 2,016 blocks based on the total computing power in the network.
Why is Bitcoin mining an important aspect?
Bitcoin mining enhances the security and decentralization of the network by preventing double-spending through the efforts of miners in solving cryptographic puzzles and validating transactions. The block reward incentivizes investment in securing the network.




