Table of Contents
Introduction
In this Bitcoin for beginners guide, we demystify the world of Bitcoin, a revolutionary digital currency that reshapes how we view and use money. Free from traditional banking and government control, Bitcoin offers a new level of financial freedom. This article simplifies Bitcoin for beginners, covering everything from its inception to how it operates and how you can securely engage with this digital currency. Embark on this journey to understand and confidently navigate the realm of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin for Beginners: The Fundamentals
Bitcoin is more than a digital currency; it’s a revolution in finance. Let’s explore its creation, control, uniqueness, and dispel common myths.

Who Invented Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an enigmatic figure or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. They introduced a decentralized digital currency, operating without the need for banks or central authorities, aiming to create a more transparent and efficient financial system. Read the original whitepaper.
Who Controls Bitcoin?
Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin isn’t controlled by any individual or entity. It’s maintained by a global network of volunteers running computers that follow a set of rules written into Bitcoin’s code, ensuring its decentralization and collective management.
Is Bitcoin Money?
Yes, Bitcoin can be considered money, but it’s a bit different from traditional forms like dollars or euros. It’s digital, meaning it exists only online. People use Bitcoin to buy goods and services, just like regular money, but it’s not controlled by any government or bank. This independence makes it unique. So, Bitcoin is like digital money with some special features.
Why is Bitcoin Different From Other Cryptocurrencies and Fiat Money?
Bitcoin stands out for its decentralized nature, limited supply of 21 million coins, and robust security. Unlike fiat currencies controlled by governments, Bitcoin operates on a transparent, immutable ledger, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation. It’s also the first successful cryptocurrency, setting the standard for others that followed.
What is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Gold?
Bitcoin and gold are both valuable but in different ways. Gold is a physical metal that has been valued for centuries and is used in jewelry, electronics, and as an investment. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is digital and relatively new. It’s valued for its technology and independence from traditional financial systems. Bitcoin has a known fixed supply and you can easily verify its authenticity, whereas there are caveats with gold. They’re both seen as ways to store value, but they’re quite different in nature.
What Are Common Misconceptions About Bitcoin?
Misconceptions about Bitcoin include beliefs that it’s used mainly for illegal activities, lacks intrinsic value, or is not secure. In reality, Bitcoin offers a secure, decentralized financial system, widely used for legitimate purposes, with value derived from its scarcity and utility. Here is a comprehensive list of Bitcoin FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt) spread over the years, that have been debunked.
Does Bitcoin Work?
Absolutely! It’s secure and operates across a network of computers worldwide. People can send and receive Bitcoins digitally. It’s especially popular for online transactions and in places where traditional banking is hard to access. The technology behind Bitcoin is complex, but it works well for what it’s designed to do. Since its inception, the Bitcoin network has worked for 99.98% of the time.
Is Bitcoin Anonymous?
Not entirely. Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the blockchain, which is public. This means anyone can see the transactions, but they won’t see your name, just your Bitcoin wallet address. However, if someone knows your wallet address, they can track your transactions. So, Bitcoin offers some anonymity, but it’s not completely hidden like some people think. It takes a bit of effort to reach higher levels of anonymity.
Is Bitcoin Legal?
In most places, yes, Bitcoin is legal. However, the rules can vary a lot from one country to another. Some countries welcome it, while others have strict regulations or even ban it. It’s important to know the laws in your area. But generally, using Bitcoin for legal transactions is okay in many parts of the world.
Can Bitcoin be Stopped or Banned?
Stopping Bitcoin entirely would be nearly impossible because it operates on a decentralized network spread across the world. However, individual countries can and have banned or restricted its use. These bans can make it hard to use Bitcoin in those places, especially for buying goods or converting it to local currency. But because of its decentralized and pseudo-anonymous nature, completely stopping Bitcoin is almost impossible as long as there’s a global internet connection.
Understanding Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin’s use is foundational to its value. Let’s dive into how transactions work, the nature of UTXOs, the purpose of addresses, transaction fees, and Bitcoin’s purchasing power.
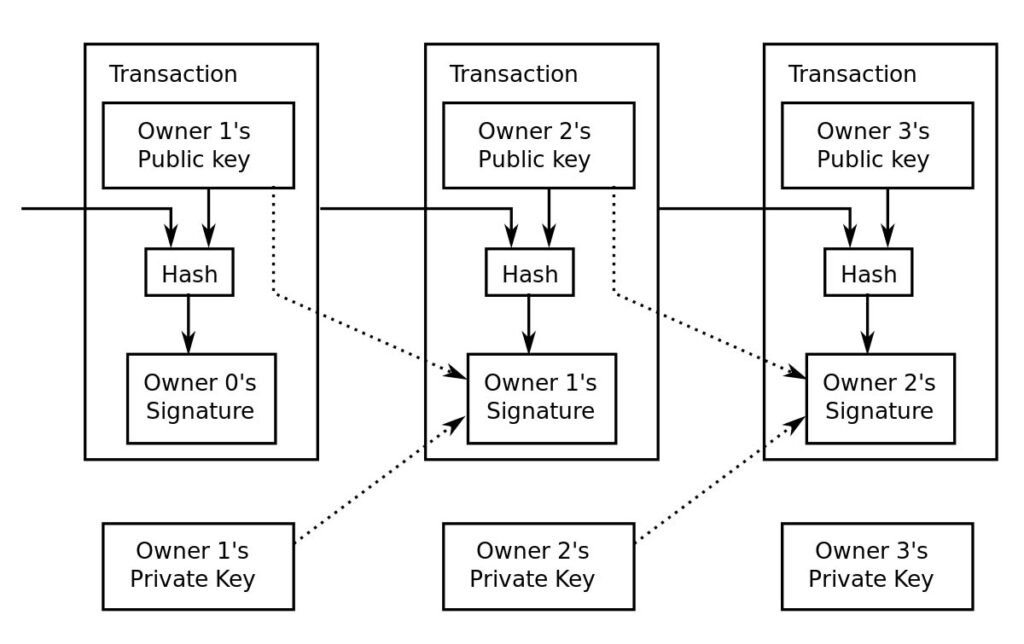
What is a Bitcoin Transaction and how does it work?
A Bitcoin transaction is a digital exchange of Bitcoin between two parties. Recorded on the blockchain, these transactions are secure, irreversible, and can be sent globally without the need for intermediaries, making Bitcoin a versatile and accessible financial tool. All you need to complete a transaction is the recipient’s address and enough bitcoin to cover your costs. It’s important to note that once a transaction is confirmed, it is irreversible!
What are Bitcoin Addresses?
Bitcoin addresses are unique strings of characters used to receive Bitcoin. They function like bank account numbers, allowing users to send and receive Bitcoin. Each address is publicly visible on the blockchain, but without directly revealing the identity of the owner, offering a balance of transparency and privacy.
What is a UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output)?
UTXO stands for Unspent Transaction Output, which is essentially the amount of leftover Bitcoin that a user has after conducting transactions. These UTXOs are tracked by the blockchain and used as inputs for new transactions, ensuring the integrity and balance of a user’s Bitcoin holdings.
Think of it as having a bunch of pieces of gold of different weights. Whatever pieces you’ve yet to spend would be considered UTXOs. Imagine now that you owe someone half an ounce of gold, but only have one in your possession. Your ounce of gold will be melted down and 2 new UTXOs will be produced: what you paid out and what you receive as change.
What are Bitcoin Transaction Fees?
Bitcoin transaction fees are small payments made to miners who process and validate transactions on the blockchain. These fees vary based on network congestion and transaction size, incentivizing miners to prioritize your transaction and ensuring the timely processing of transfers.
What are Bitcoin Exchanges?
Bitcoin exchanges are like digital marketplaces where you can buy and sell Bitcoin using different currencies. They’re websites or apps that connect buyers and sellers. You can exchange your dollars, euros, or other currencies for Bitcoins and vice versa. These platforms also show the current market price of Bitcoin. It’s important to use a reputable exchange, as security is a big concern in the world of digital currencies.
What can I buy with Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s acceptance is growing globally, allowing users to buy a variety of goods and services. From online shopping to travel bookings and even real estate, Bitcoin’s versatility as a payment method is continuously expanding, reflecting its increasing integration into mainstream commerce. Take a look at BTC Map to find physical locations which accept bitcoin as payment.
Securely Storing Bitcoin
Secure storage is crucial for Bitcoin. We’ll explore wallet types, the concept of a wallet, multi-signature security, and the principles of hot and cold storage.
What is a Bitcoin wallet?
A Bitcoin wallet is a digital tool to store, send, and receive Bitcoin. It manages your Bitcoin addresses and private keys, the latter being essential for authorizing transactions. The security of a Bitcoin wallet is paramount, as it safeguards your digital assets against unauthorized access.
What is a Bitcoin Private Key?
A Bitcoin private key is a secret 256-bit number that acts as a password to a Bitcoin address, allowing the owner to sign and authorize transactions. Nowadays, it’s essentially represented by a list of 12, 18 or 24 words. It’s crucial for security and must be kept confidential, as anyone with access to it can control the associated Bitcoins. The complexity of the key ensures its near impossibility to be guessed, safeguarding the user’s assets.
What are the Different Types of Bitcoin Wallets?
Bitcoin wallets come in various forms: software wallets on computers and smartphones, hardware wallets for offline storage, and paper wallets as physical printouts. Each type offers different levels of security and accessibility, catering to the diverse needs of users.
What is a Multi-Signature Scheme?
Multi-signature, often abbreviated as multisig, refers to a security feature that requires multiple parties to sign off on a transaction before it can be executed. This adds an extra layer of security, making it ideal for shared accounts or enhancing individual account protection. Although it does come with added complexity, security, and fee considerations.
What is Hot and Cold storage?
Hot storage refers to keeping Bitcoin in wallets connected to the internet, offering convenience but higher risk. Cold storage involves storing Bitcoin offline, like in hardware wallets, providing enhanced security against online threats.
What is a Passphrase?
A passphrase in Bitcoin is an additional security layer for wallets. It acts like an extended password, offering extra protection against unauthorized access, especially important in securing recovery phrases for wallet backups. Read “Everything You Need To Know About Passphrases”, an article I wrote, for more information.
The Bitcoin Network and Blockchain
Understanding the Bitcoin network is key to grasping its strength. We’ll cover the role of nodes, the blockchain, consensus rules, and the transaction verification process.
What is the Role of a Bitcoin Node?
Nodes are crucial components of the Bitcoin network. They independently validate transactions and blocks, maintaining the blockchain’s integrity and security. By storing and broadcasting the blockchain, nodes ensure the decentralized nature of Bitcoin. Running your own Node is possible and accessible to many.
What are consensus rules?
Consensus rules in Bitcoin are the guidelines that nodes follow to agree on the state of the blockchain. These rules ensure that all participants have a consistent view of the transaction history, maintaining the network’s integrity and trustlessness.
What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain in Bitcoin is a digital ledger that records all transactions chronologically and publicly. Each block contains a group of transactions, linked to previous blocks, creating a secure and immutable chain, making it virtually impossible to alter past transactions.
What is a Block?
A block is a set of data containing a batch of valid transactions that have been verified and agreed upon by the network participants. Each block includes a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a linked chain that confirms the integrity of the preceding blocks.
This chain of blocks forms the blockchain, which serves as a public ledger for all transactions in the network. In Bitcoin, blocks are added approximately every ten minutes through a process called mining, which involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles. This structure ensures the security and continuity of the blockchain, making it resistant to tampering and revision.
What is the Process of Verifying a Bitcoin Transaction?
Verifying a Bitcoin transaction involves checking its validity against the blockchain history. Miners play a key role in this, ensuring transactions are legitimate and adding them to the blockchain, while nodes confirm and propagate the updated blockchain information.
Bitcoin Mining and Network Security
Mining secures Bitcoin and facilitates its operation. We’ll delve into mining, confirmations, who can mine, mining pools, Bitcoin’s security features, and the significance of halving.

What is Byzantine Generals Problem?
Conceptualized in 1982 by Leslie Lamport, Robert Shostak, and Marshall Pease (see the paper), it is a dilemma in distributed computing that illustrates the difficulty of reaching consensus in a system where some participants may be unreliable or malicious.
It involves a group of generals, some of whom might be traitors, needing to agree on a unified battle strategy. The challenge lies in creating an algorithm where all loyal generals reach the same decision, despite the presence of deceitful elements.
This problem is pivotal as it mirrors the need for consensus in a decentralized network like Bitcoin, where nodes must agree on the state of the ledger while ensuring security and resilience against dishonest actors. Bitcoin addresses this issue through its proof-of-work mechanism, enabling a reliable and tamper-proof consensus among participants.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. This process is also known as Proof-of-Work. Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles, requiring substantial computational power, to secure the network and are rewarded with new Bitcoin and transaction fees.
What is a Confirmation?
A confirmation in Bitcoin occurs when a transaction is included in a block and added to the blockchain. Each subsequent block added provides an additional confirmation, increasing the security and irreversibility of the transaction. Learn more about why confirmations are required here.
Who Can Mine Bitcoin?
Anyone with access to the necessary hardware, software and energy can mine Bitcoin. It involves setting up a mining rig, which requires computational power and electricity, and participating in the network’s transaction validation process. Note that it is incredibly difficult to mine Bitcoin, which is why miners tend to join a mining pool.
What is a Mining Pool?
A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computational resources to increase their chances of successfully mining Bitcoin. They share the rewards proportionally to the contributed processing power, offering a more consistent payout than mining solo.
Can Bitcoin be Hacked or Counterfeited?
Bitcoin’s architecture makes it incredibly resilient against hacking and counterfeiting. The decentralized network, cryptographic security, and consensus mechanisms ensure the integrity and authenticity of each Bitcoin, making fraudulent activities nearly impossible.
What is the Bitcoin Halving?
The Bitcoin Halving is an event that occurs every 210,000 blocks or approximately every four years, where the reward for mining new blocks is halved. It’s a built-in feature to control Bitcoin’s supply, affecting the rate of new Bitcoin creation and, potentially, its market value.
Governance and Evolution of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s evolution involves rules and updates. We’ll explore how updates occur, the nature of forks, and the innovative Lightning Network.
How is Bitcoin Updated?
Bitcoin is updated through a community-driven process. Proposals for changes, known as BIPs (Bitcoin Improvement Proposals), are debated and implemented when there’s widespread consensus among network participants, reflecting Bitcoin’s democratic and decentralized ethos. Find the list of BIPs here.
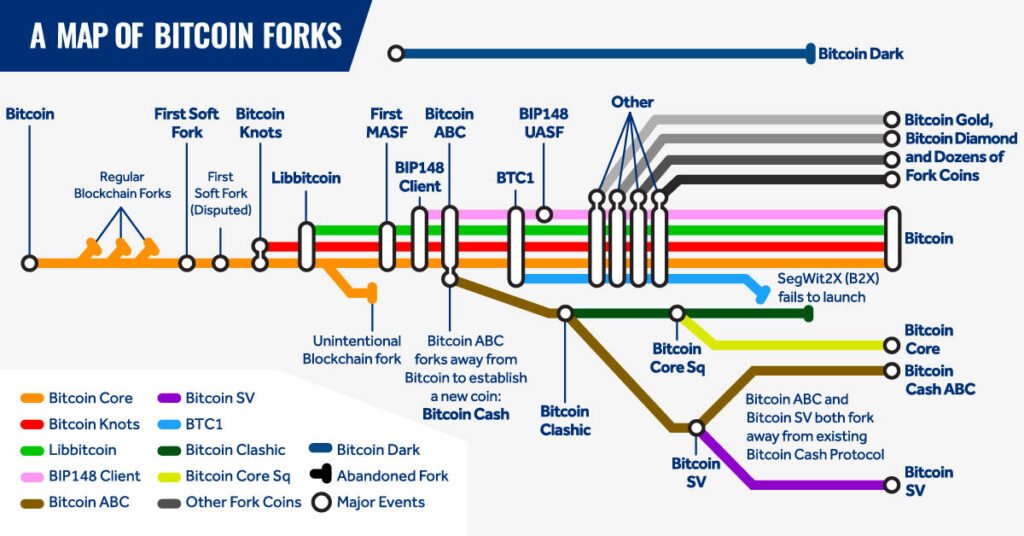
What is a Bitcoin Fork?
A Bitcoin fork occurs when changes in the protocol lead to diverging paths on the blockchain. Soft forks are backward-compatible changes, while hard forks create a new blockchain version, leading to the creation of a new cryptocurrency.
What is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain. It enables faster, cheaper transactions by allowing off-chain transactions, with periodic settlements on the main blockchain, enhancing Bitcoin’s scalability and utility for everyday transactions.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is not just a currency; it’s a new financial paradigm. Understanding its basics empowers you to navigate this exciting space, embracing the possibilities of decentralized digital currency. Having journeyed through the essentials of Bitcoin, from its core principles to its transaction dynamics and security measures, we conclude our primer.
This exploration has highlighted Bitcoin’s significance beyond a digital currency, embodying a shift towards a more decentralized financial future. As the Bitcoin landscape continually evolves, staying informed and engaged in curcial.
This guide marks the start of your Bitcoin journey, opening doors to a world ripe with innovation and opportunity in the unfolding future of finance. Feel free to read this article too, to go a little deeper into some of the concepts explored above.










