Welcome to the Bitcoin 101. In this article, the general concept of Bitcoin is explained, so the newcomers to Bitcoin could get a general idea about what Bitcoin is, how it works, and why it matters.
Table of Contents
Bitcoin 101: The Genesis of a New Financial Era
Bitcoin marks the beginning of a new era in finance, emerging in 2009 as a response to the fragile and centralized nature of traditional financial systems. Created by an entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced a decentralized digital asset, operating independently of central authorities.
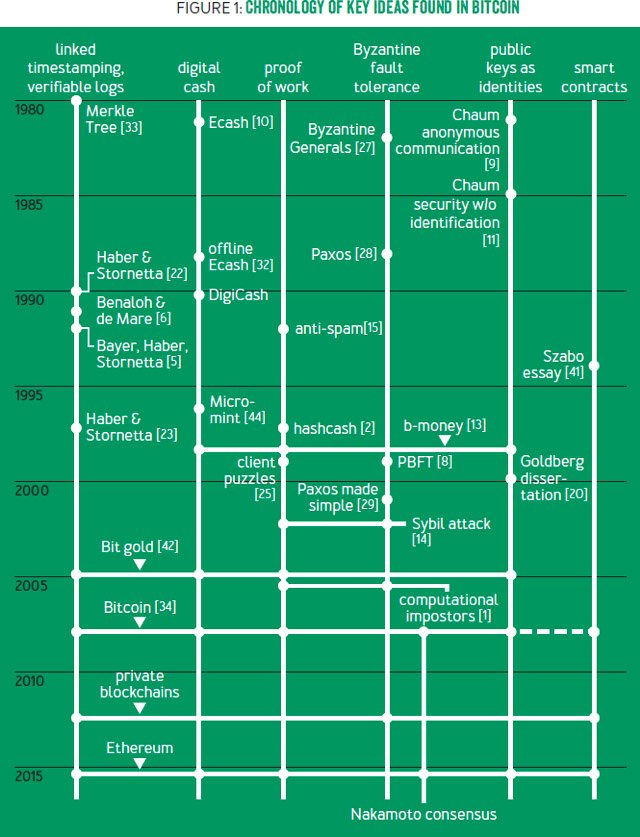
Built on Decades of Efforts
The creation of Bitcoin didn’t occur in a vacuum. It stands on the shoulders of decades of technological advancements and cryptographic research. Prior digital currency attempts, like b-money and Bit Gold, laid foundational concepts that Bitcoin would later refine. Breakthroughs in cryptography, such as public-key cryptography, provided the tools necessary for secure, decentralized digital transactions, leading up to the birth of Bitcoin.
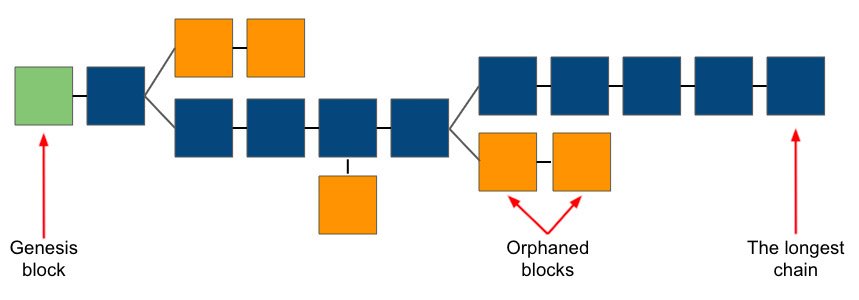
The Nakamoto Consensus
At the heart of Bitcoin’s operation is the Nakamoto Consensus, a novel approach that combines proof-of-work (PoW) with decentralized decision-making. Miners, using computational power, solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain, earning bitcoin as a reward. This process ensures network security and transaction integrity, solving the Byzantine Generals’ Problem in a decentralized context.
Node and Consensus Rules
Nodes, running the Bitcoin software, play a crucial role in maintaining the network’s health and consensus. They enforce key rules, such as:
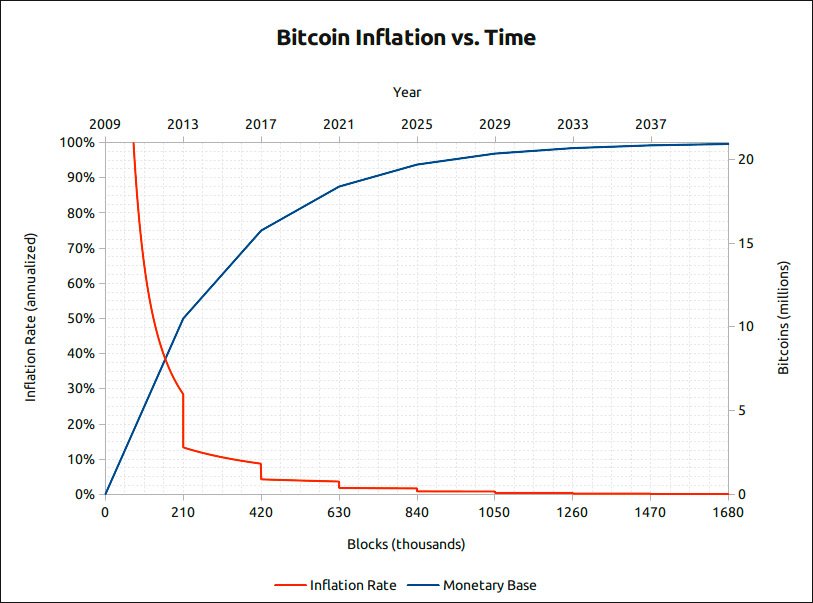
- Supply Cap: Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, ensuring scarcity and value preservation.
- Issuance Schedule: New bitcoin are introduced at a predictable rate, halving approximately every four years, mimicking the diminishing returns of mining physical commodities such as gold.
- Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs): These are suggestions for improvements to the Bitcoin protocol, vetted through a rigorous community review process.
- Soft and Hard Forks: Forks represent changes to the protocol. Soft forks are backward-compatible changes, whereas hard forks are not and can lead to network splits.
- No Double-Spend: Ensuring each bitcoin can only be spent once, maintaining the currency’s integrity and trust.
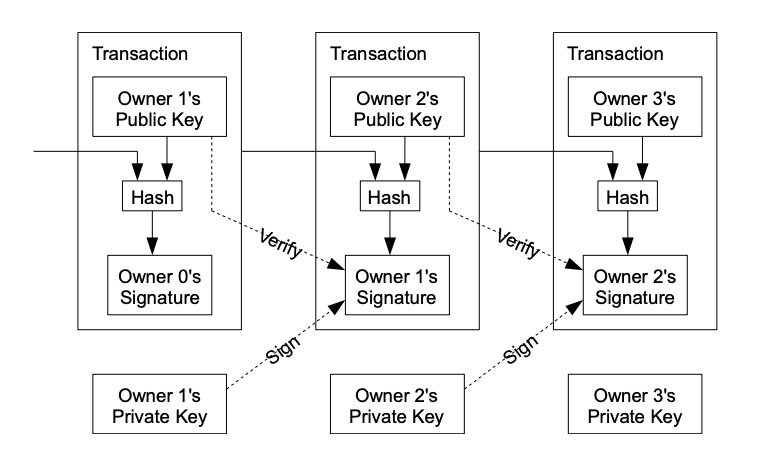
Public and Decentralized Ledger
Bitcoin’s blockchain serves as a public ledger, recording every transaction transparently and immutably. This decentralized ledger ensures that transactions are secure, transparent, and irreversible, unlike traditional banking systems where records can be altered.
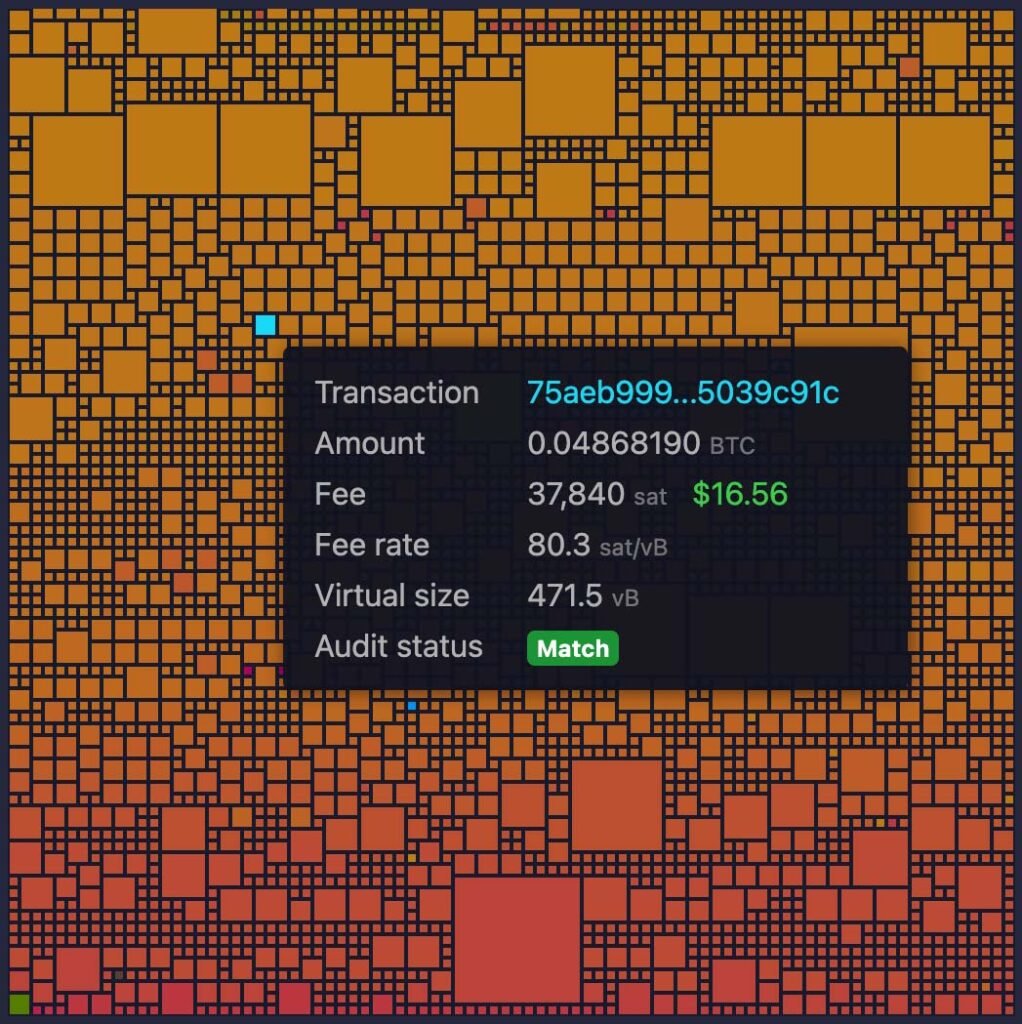
Storing and Transacting
Bitcoin ownership is represented through digital keys, which are stored in digital wallets. These wallets, which are typically software or hardware-based, generate and secure the cryptographic keys needed to access Bitcoin addresses and execute transactions.
It’s not the bitcoin themselves that are stored in these wallets, but rather the keys that provide control over the bitcoin on the blockchain. This design ensures that only the wallet owner can access and transact with their bitcoin, providing a secure and direct way to manage digital assets without reliance on intermediaries.
Scaling
As Bitcoin adoption grew, so did the need for scaling solutions. Some include:
- Lightning Network: This is a second-layer protocol that enables fast and low-cost transactions off the main blockchain, resolving some of the scalability issues.
- Taproot: Implemented to enhance privacy and efficiency, Taproot allows for more complex transactions at a lower cost.
- Schnorr Signatures: These signatures enable more complex and privacy-preserving transaction capabilities, contributing to scalability and security.
Philosophical Underpinnings
Beyond its technological prowess, Bitcoin embodies a philosophical revolution. It challenges conventional views on money and sovereignty. In a financial world dominated by centralized institutions, Bitcoin presents an alternative: a decentralized, accessible form of money.
Related reading: Freedom Money, God’s Money

It empowers individuals, fostering financial inclusion and challenging the status quo of financial systems. In essence, Bitcoin is not just a currency or a technology; it’s a movement toward a more open, transparent, and equitable financial future.
FAQ
u003cstrongu003eWhat is Bitcoin?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital asset created in 2009 as an alternative to traditional financial systems. It matters because it challenges the centralized nature of finance, offering a transparent, secure, and inclusive form of money.
u003cstrongu003eWho created Bitcoin?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin was created by an anonymous person or group, known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Their identity isn’t known to this day.
Wu003cstrongu003ehat is the Nakamoto Consensus?u003c/strongu003e
The Nakamoto Consensus is a unique approach that combines proof-of-work with decentralized decision-making, ensuring network security and transaction integrity.
Du003cstrongu003eoes Bitcoin use previous technological advancements?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin builds on decades of technological progress, including prior digital currency attempts like b-money and Bit Gold. Breakthroughs in cryptography, such as public-key cryptography, paved the way for secure and decentralized digital transactions.
u003cstrongu003eWhat role do nodes play in the Bitcoin network?u003c/strongu003e
Nodes enforce key rules in the Bitcoin network, including supply cap, issuance schedule, Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs), and rules regarding soft and hard forks. They are essential for maintaining the health and consensus of the network.
u003cstrongu003eHow is Bitcoin different from traditional banking systems?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin’s blockchain serves as a public ledger that is decentralized, transparent, and immutable. This ensures secure and irreversible transactions, in contrast to traditional banking systems where records can be altered.
u003cstrongu003eHow are Bitcoin transactions stored and executed?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin ownership is represented through digital keys stored in digital wallets. These wallets, whether software or hardware-based, secure the cryptographic keys needed to access Bitcoin addresses and execute transactions.
u003cstrongu003eWhat are some scaling solutions adopted by Bitcoin?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin has implemented scaling solutions such as the Lightning Network for faster and low-cost transactions, Taproot for enhanced privacy and efficiency, and Schnorr Signatures for more complex and privacy-preserving transaction capabilities.
u003cstrongu003eWhat does Bitcoin change about money?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin represents a philosophical revolution by challenging the dominance of centralized institutions in the financial world. It empowers individuals, fosters financial inclusion, and offers an alternative vision for a decentralized and equitable financial future.
u003cstrongu003eWhat is the significance of the fixed supply of 21 million bitcoins?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins to ensure scarcity and value preservation. This mimics the diminishing returns of mining physical commodities like gold, contributing to Bitcoin’s unique economic model.
Is Bitcoin just a currency?
Bitcoin is not merely a currency or technology; it’s a movement toward a more open, transparent, and equitable financial future. It embodies a shift in philosophy, challenging the status quo and promoting financial empowerment for individuals.
Related reading:










