Understanding the foundational elements of Bitcoin is crucial for beginners. This Bitcoin for dummies guide breaks down the immutable ledger of the blockchain, the crucial role of key pairs, the competitive world of mining, and the secure storage provided by Bitcoin. Additionally, the guide explores the concept of Bitcoin Halving, a unique method designed to control inflation and reinforce its scarcity.
Blockchain
Think of the blockchain as a big book that keeps track of all the times people have sent or received bitcoin. Each transaction is written on a page of this book. When a page is filled with transactions, it gets added to a stack of other filled pages. Everyone can see this book and what’s written in it, but no one can erase or change the pages once they’re added. This makes it tough for anyone to cheat because to change any information, you’d need to rewrite the whole stack in many different books at the same time, and everyone would notice.
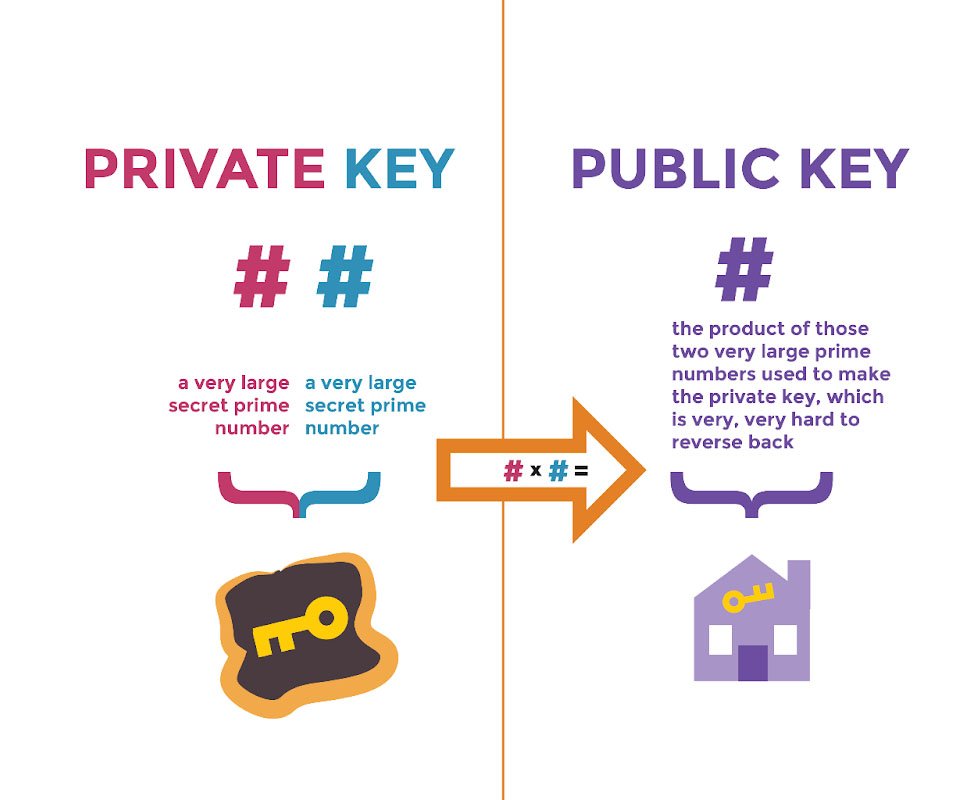
Key Pairs
Key pairs work like a combination of a mailbox and a secret code. Your mailbox (public key) is what you give to people so they can send you bitcoin. Your secret code (private key) is what lets you open your mailbox and send bitcoin to others. It’s crucial to keep your secret code safe because if someone else finds it, they can send your bitcoin away without your permission.
Mining
Mining is similar to playing a very intense, competitive game where people use their computers to solve a guessing puzzle. The first person to solve the puzzle gets to add a new page to the big book of transactions (this is called adding a block to the blockchain). As a reward for their hard work, they get some bitcoin. This process helps keep the system honest because it confirms that all the transactions are real, and by giving out new bitcoin, it also slowly increases the amount of bitcoin in circulation.
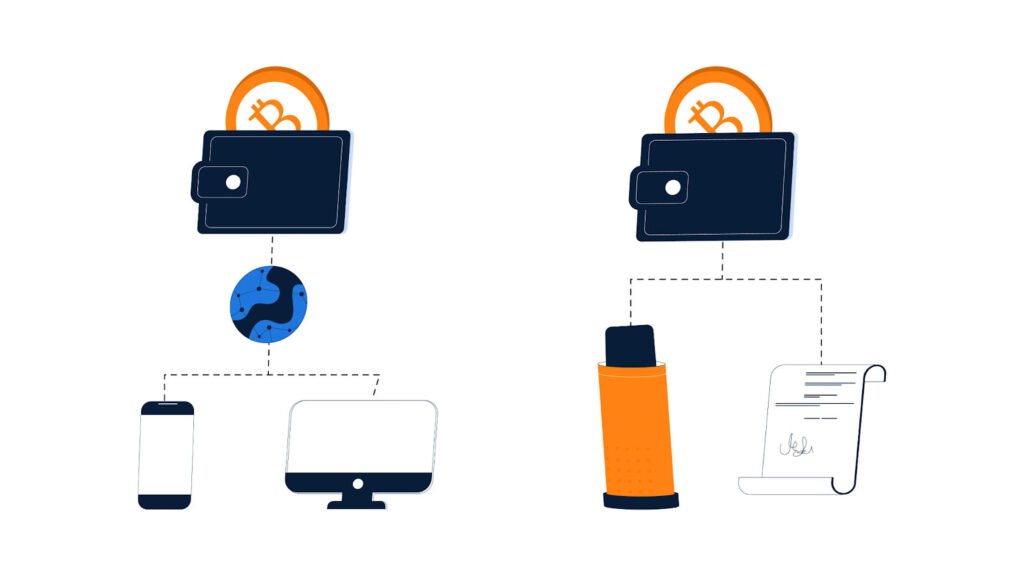
Wallets
In the Bitcoin world, a wallet is where you keep your key pairs, which let you access your bitcoin. Unlike a regular wallet, which holds things like cash and cards, a Bitcoin wallet doesn’t store the bitcoin itself—instead, it holds the keys you use to access your bitcoin on the blockchain and manage transactions. You can have a wallet on your computer, your phone (called hot wallet), or even a special offline device meant just for Bitcoin(cold storage). Protecting your wallet is critical because if you lose access to your keys, you can’t access your bitcoin.
- Hot Wallets: Connected to the internet; convenient for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to security threats.
- Cold storage/Wallets: Offline storage (like hardware devices or paper wallets); offers higher security by being less accessible to online hackers but is less convenient for regular use.
Bitcoin’s Halving
“Bitcoin Halving is an event programmed into the Bitcoin protocol that occurs approximately every four years or 210,000 blocks. During this event, the reward that miners receive for confirming transactions and securing the network is halved.
This reduction in rewards ultimately decreases the rate at which new bitcoin is created, enforcing scarcity. The purpose of the Bitcoin Halving is to control the inflation rate of Bitcoin and ensure that the total supply remains limited to 21 million, making it a deflationary asset over time.”
– BitcoinNews

Bitcoin For Dummies: Summary
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009 by an unknown person using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, stands out as the first decentralized digital currency. Unlike traditional currencies controlled by central banks, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network that spans numerous computers worldwide. This network leverages blockchain technology—a type of public ledger that records all transactions openly and immutably—to maintain security and transparency without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Bitcoin is unique not only because it is digital and not issued by any central authority, but also because it has a predetermined limit on quantity. There can only ever be 21 million bitcoin, a measure designed to prevent inflation and mimic the scarcity of precious metals. Bitcoin is created through a process known as mining, where individuals use powerful computers to solve a guessing puzzle. Successful miners help process transactions and secure the network, and in return, they are rewarded with new bitcoin. This reward diminishes over time with an event referred to as “halving,” which gradually reduces the rate at which new bitcoin are introduced to the system.
Andreas Antonopoulos provided a compelling introduction to Bitcoin seven years ago, explaining why civilization is shifting towards a cashless society and the significant role Bitcoin could play in the lives of future generations. He detailed the technological and societal trends leading us away from traditional paper and coin money, emphasizing how Bitcoin, with its decentralized and digital nature, offers a revolutionary alternative. Antonopoulos argued that Bitcoin not only aligns with the global trend towards digital transactions but also provides an inclusive financial system that could empower people worldwide, particularly those without access to traditional banking.
A great starting point for beginners is the Bitcoin for dummy Guide by Luc Fiore called ‘Bitcoin 101’, available as a PDF. This guide offers a clear and comprehensive introduction to Bitcoin, covering essential concepts and addressing common misconceptions. It provides readers with a solid foundation in understanding how Bitcoin works and its potential impact on the financial world.










