Bitcoin has revolutionized the way we think about and execute financial transactions. As its popularity grows, so does the curiosity about the intricacies of its operation.
If some points are not considered when sending bitcoin, transactions might take a long time to confirm. Unaware users might get frustrated and ask “how long does bitcoin take to send?!”
Understanding the factors influencing Bitcoin transaction times can help users manage their expectations and navigate the Bitcoin network more efficiently.
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
Before diving into transaction times, it’s essential to understand how Bitcoin transactions work. When you send bitcoin, your transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, where it must be verified and added to the blockchain. This process involves several steps:
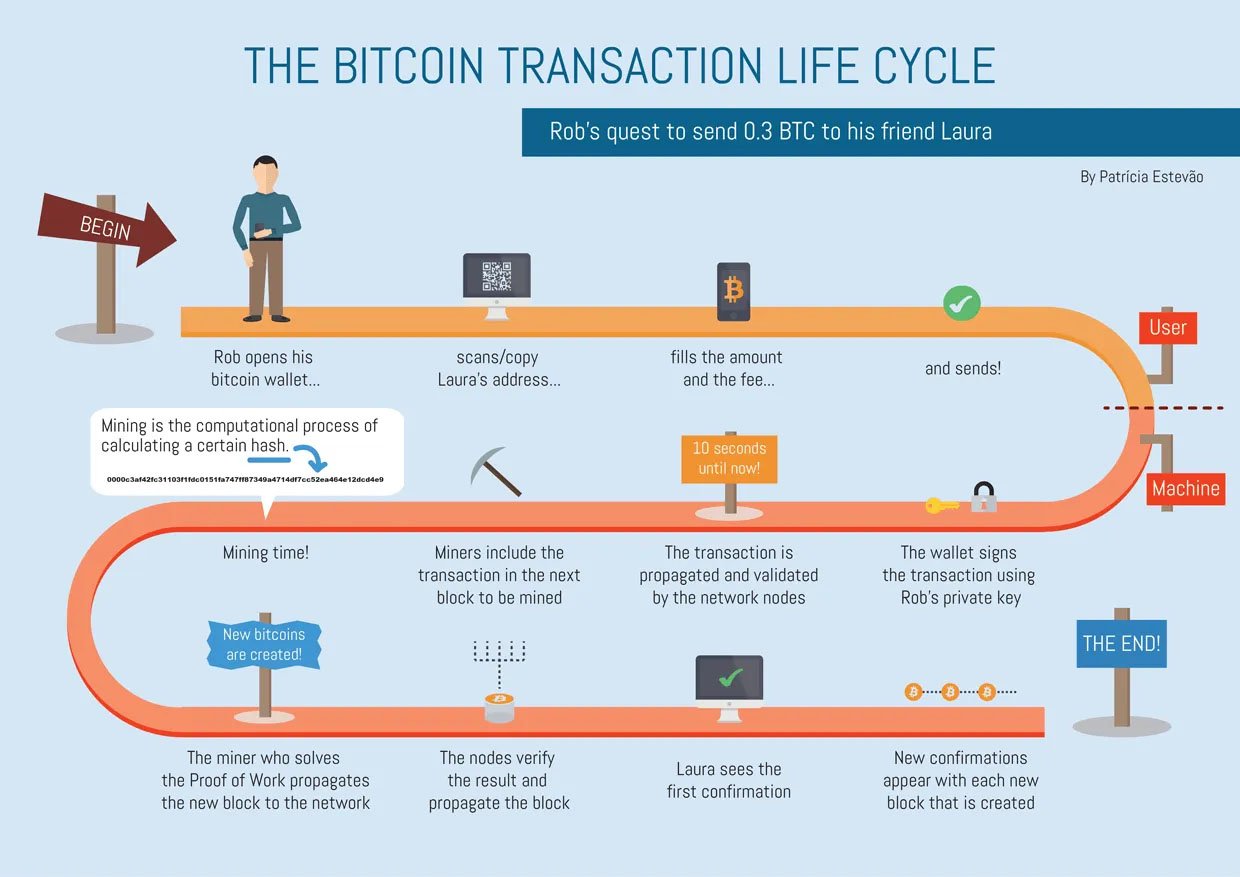
- Broadcasting: When a transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, where it is picked up by miners.
- Verification: Miners verify the transaction to ensure that the sender has sufficient bitcoin and that the transaction’s signature is legitimate.
- Inclusion in a Block: Once verified, the transaction is included in a block, which is then added to the blockchain.
- Confirmations: The transaction must receive confirmations. Each confirmation represents the addition of a new block to the blockchain after the block containing your transaction.
How Long Does Bitcoin Take To Send On Average?
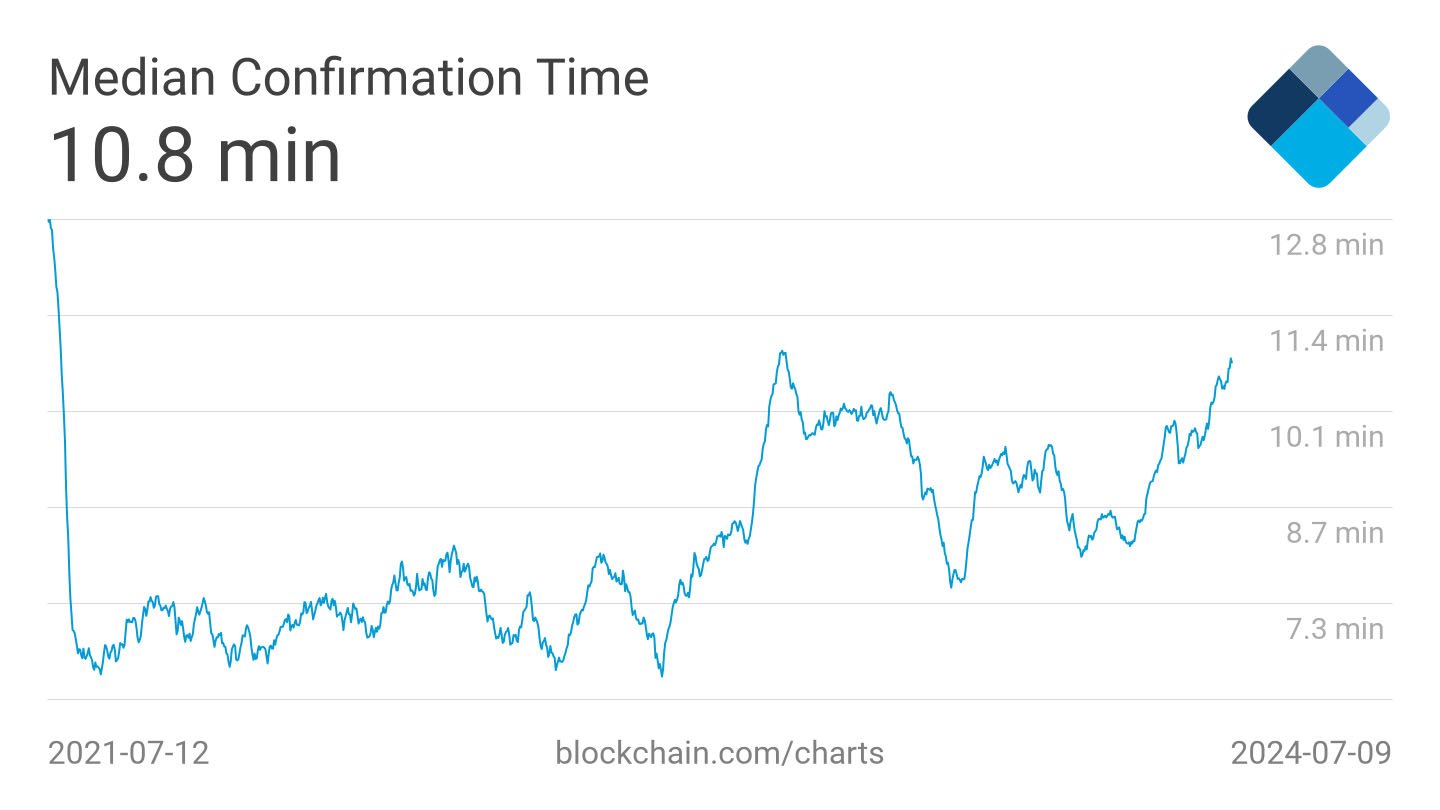
The average time it takes to send bitcoin can vary significantly depending on several factors. Typically, a Bitcoin transaction can take anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours to be confirmed.
Most transactions are confirmed within 10 minutes to an hour. However, under certain conditions, this time can be shorter or longer.
Factors Influencing Transaction Time
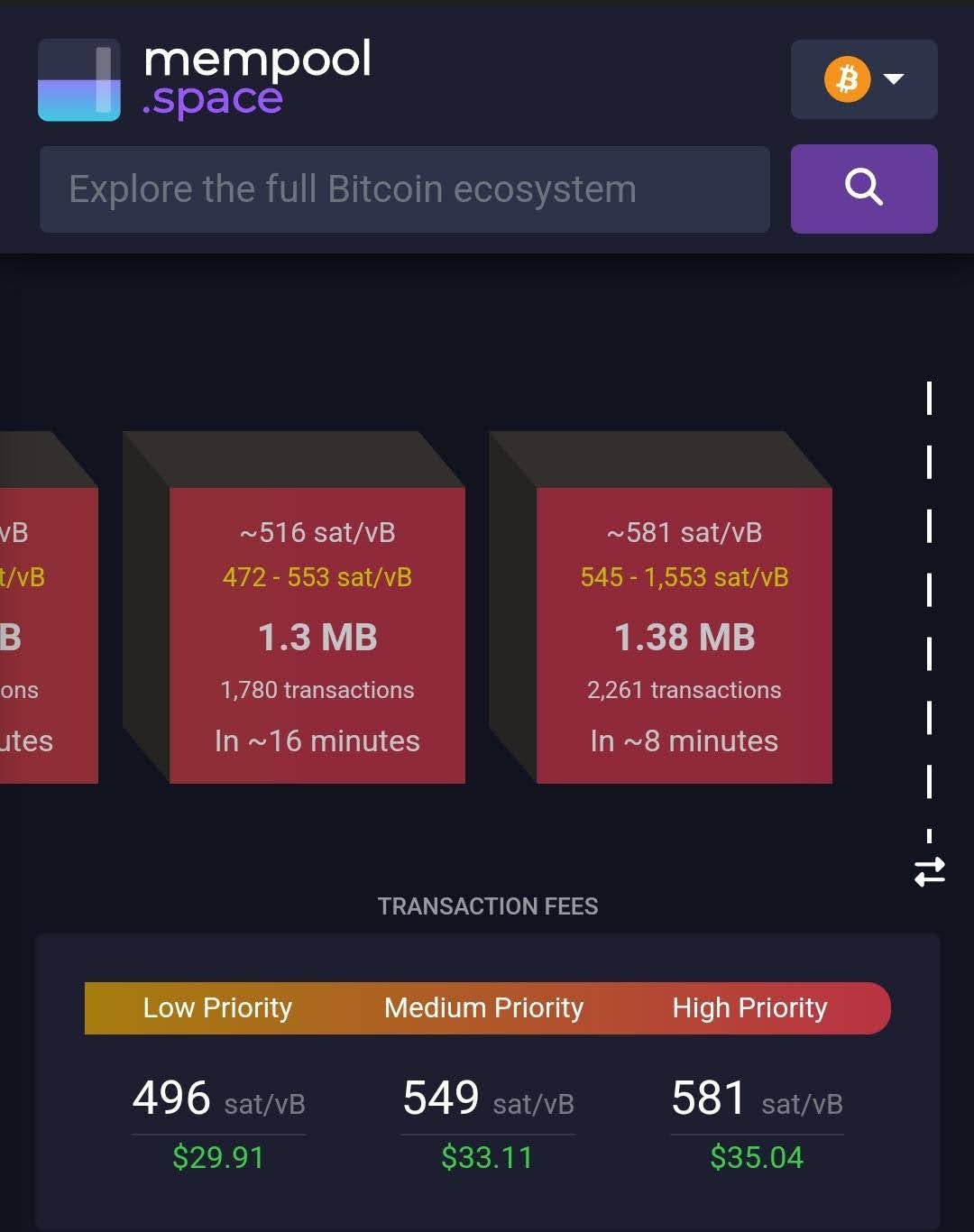
- Network Congestion: One of the primary factors influencing Bitcoin transaction times is network congestion.
During periods of high demand, such as during price surges or market crashes, the number of transactions waiting to be processed can exceed the network’s capacity. This congestion leads to longer wait times as transactions queue up for processing. - Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions include fees paid to miners for verifying and adding the transaction to the blockchain. Higher fees incentivize miners to prioritize certain transactions.
Users who pay higher fees can expect faster transaction confirmations, while those who pay lower fees might experience delays. - Change in Miner Activity: The number of active miners and the overall change in hash rate of the network can influence transaction times.
If the hash rate of the network increases suddenly after a difficulty adjustment, more computational power is available to process transactions, potentially speeding up confirmation times.
Conversely, if the hash rate declines, the network might process transactions more slowly.
This trend continues until the next difficulty adjustment, which adjusts the difficulty in a way that median block confirmation time returns to 10 minutes. - Transaction Confirmation Threshold: Different transactions require different numbers of confirmations before being considered final.
While one confirmation might be sufficient for small transactions, larger transactions or those involving significant value might require multiple confirmations, leading to longer wait times.
Related: How Many Confirmations Are Needed For a Bitcoin Transaction?
Strategies to Speed Up Bitcoin Transactions
For users looking to expedite their Bitcoin transactions, there are several strategies to consider:
- Pay Higher Fees: By opting to pay a higher transaction fee, users can incentivize miners to prioritize their transactions. Various Bitcoin wallets allow users to set custom fees based on current network conditions.
- Transaction Accelerators: Some services, known as transaction accelerators, allow users to pay an additional fee to prioritize their transactions. These services work by partnering with mining pools to include the transaction in the next available block.
- Optimal Timing: Sending transactions during off-peak times can help avoid network congestion and lead to faster confirmations. Monitoring network conditions and timing transactions accordingly can be beneficial.
- Batching Transactions: For users who frequently send multiple transactions, batching them into a single transaction can save on fees and reduce overall network congestion, leading to faster processing times.
- Segregated Witness (SegWit): Utilizing SegWit addresses can reduce the size of the transaction and lower fees, making it more attractive for miners to include it in the next block.
Real-World Implications
Understanding Bitcoin transaction times is crucial for merchants, individuals, and high-stakes environments. Knowing average transaction times helps manage expectations and plan transfers or trades.
Users must balance speed and cost, especially during network congestion. Layer 2 solutions, like the Lightning Network, are essential for faster and cheaper transactions, improving efficiency and scalability.
Conclusion
Bitcoin transaction times are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including network congestion, transaction fees, block size, and miner activity.
While the average transaction can take anywhere from 10 minutes to over an hour, understanding these variables can help users navigate the Bitcoin network more effectively.
By employing strategies such as paying higher fees, using transaction accelerators, timing transactions during off-peak hours, batching transactions, and utilizing SegWit, users can optimize their transaction experience.
As the Bitcoin network continues to evolve and scalability solutions are implemented, transaction times may become more predictable, further enhancing Bitcoin’s usability as a global digital currency.










