When you first start using Bitcoin, you might come across the term “confirmations.” This concept is fundamental to how Bitcoin transactions work, ensuring their security and immutability.
This article explores what confirmations are, and how many confirmations for bitcoin transactions are necessary. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
A confirmation for a transaction occurs when a it is included in a block, and added to the blockchain.
The blockchain is a public ledger where all Bitcoin transactions are recorded. When you make a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to the network and waits to be included in a block by miners.
Miners are participants in the network who use computational power to find a very difficult random number called a “nonce”. When a miner successfully finds it, they can add a new block to the blockchain, and any transactions within that block receive their first confirmation.
With any block added after that, that transaction receives an additional confirmation.
Let’s look at an example, which has been prepared when the Bitcoin blockchain was at height 848,629. It means that 848,629 blocks have been mined since Bitcoin’s inception in 2009.

We follow a transaction with TXID of 06e405af33622fd8ae8517ae8891a002bdb2c349da1703ad301584a24739399d. This transaction was in mempool and was not confirmed in the beginning. It means it was not included in any blocks.
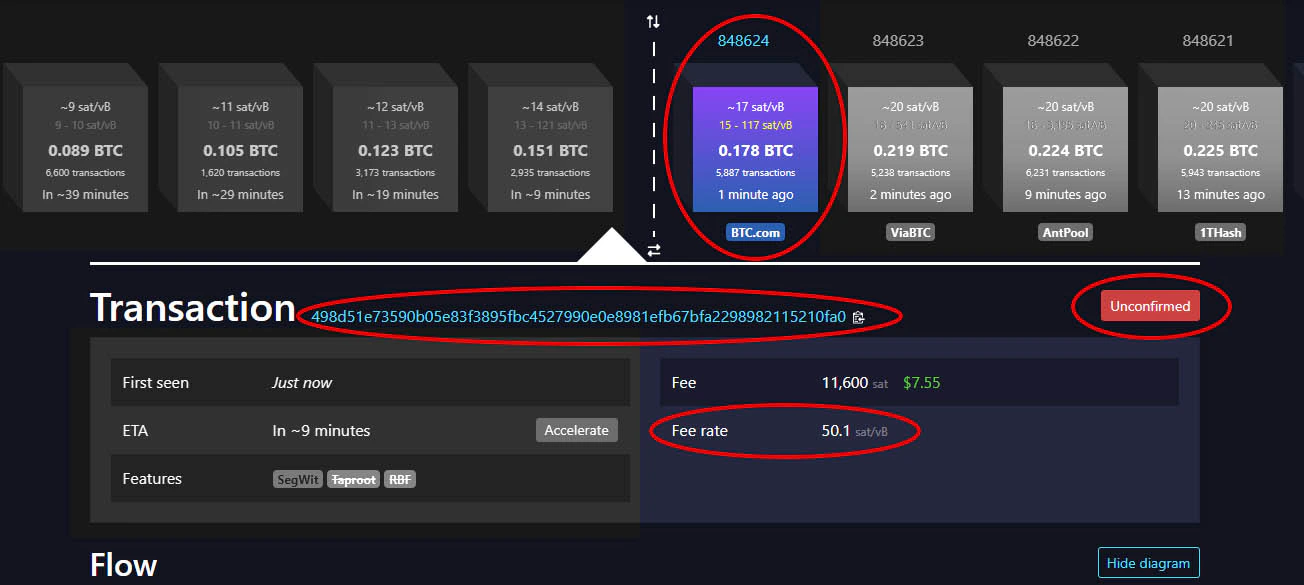
With the fee the transaction was willing to pay, it could be confirmed and included in the next block.

Once the next block was mined, it becomes evident that the transaction was included in it, granting it its first “confirmation”. As the blocks keep getting mined and added to the blockchain, the transaction’s confirmation count keeps increasing.

Confirmations are crucial because they verify that a transaction is legitimate and prevent double-spending.
Double-spending is a potential issue where the same bitcoin could be spent more than once. Each confirmation makes it exponentially more difficult to reverse the transaction, thereby securing it against fraud.
The number of confirmations required depends on the level of security you need and the value of the transaction:
1 Confirmation: One confirmation is usually sufficient for small transactions, like buying a coffee. This takes about 10 minutes on average, as a new block is added to the blockchain approximately every 10 minutes.
3 Confirmations: This is often used for medium-sized transactions, such as purchasing goods or services online. Three confirmations provide a higher level of security, taking about 30 minutes.
6 Confirmations: For larger transactions, such as buying a car or transferring large amounts of money, six confirmations are considered the gold standard. At six confirmations, the probability of a transaction being reversed is incredibly low, making it extremely secure. This typically takes around an hour.
The rule of thumb in the Bitcoin community is to wait for six confirmations for high-value transactions.
This is because after six confirmations, the transaction is deeply embedded in the blockchain, and it would require an enormous amount of computational power to reverse it, making it virtually impossible.
When you send or receive bitcoin, most wallets and exchanges will show the number of confirmations a transaction has received. You can also use a block explorer such as mempool.space, which is an online tool that lets you view details about Bitcoin transactions and blocks.
Understanding Bitcoin confirmations is essential for anyone using Bitcoin. It ensures that your transactions are secure and helps you gauge the appropriate level of security needed for different types of transactions.
By waiting for the right number of confirmations, you can confidently use Bitcoin, knowing that your transactions are safe and immutable.
Bitcoin’s confirmation system is a testament to its robust security model, making it the most reliable and secure form of digital money. As you become more familiar with it, you’ll appreciate the importance of confirmations in maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the Bitcoin network.










