In the world of digital finance, Bitcoin stands as the gold standard. It’s not just a currency; it’s a revolution against centralized control, inflation, and inefficiency.
Those ready to join this revolution are taking a crucial step toward financial sovereignty. Here’s a detailed guide to help navigate this process seamlessly by explaining how to send bitcoin to another wallet.
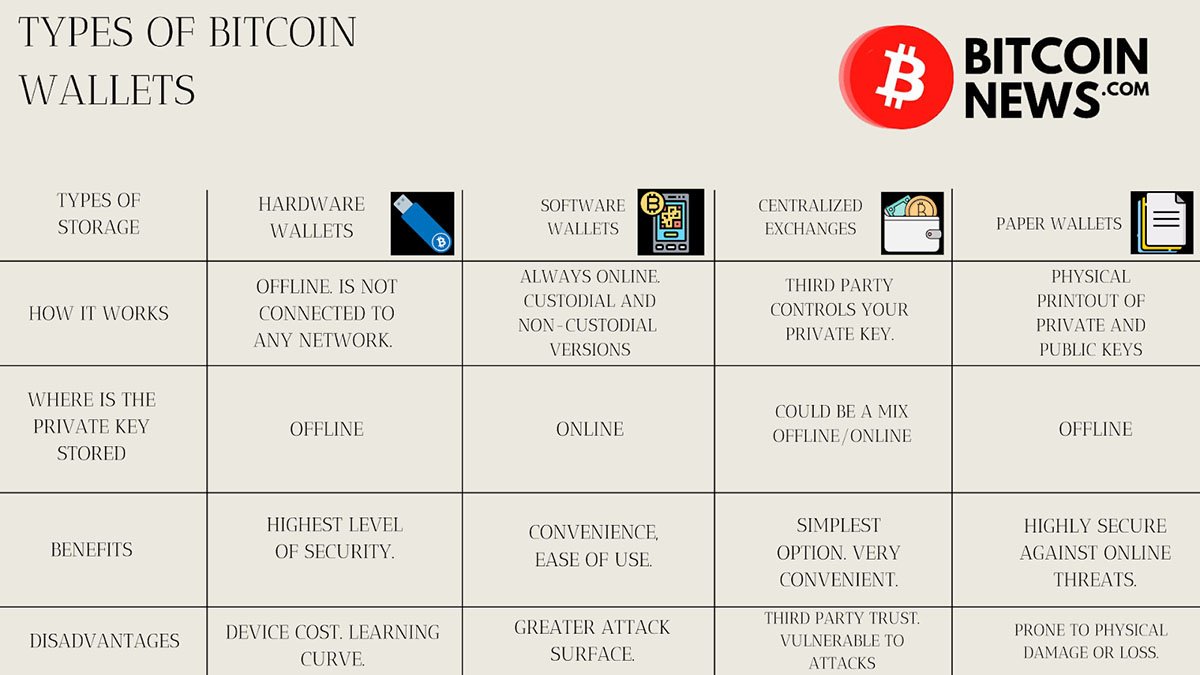
Understanding Bitcoin Wallets
Before diving into the mechanics of sending bitcoin, it’s essential to understand what a Bitcoin wallet is. A Bitcoin wallet is a tool that allows users to store, send, and receive bitcoin. There are several types of wallets, including:
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices like ColdCard, Jade or BitBox02 store bitcoin offline, providing the highest level of security.
- Software Wallets (Desktop or Mobile): Applications that can be installed on a computer or smartphone, such as Electrum or Zeus.
- Centralized Exchanges: Online services that store bitcoin, also known as centralized exchanges, like Swan Bitcoin or River.
- Paper Wallets (not recommended): Physical pieces of paper with private and public keys printed on them.
This guide assumes that the user has already set up a wallet and has bitcoin in it.
Related: What is a Bitcoin Wallet? An In-Depth Guide
Prerequisites for Sending Bitcoin
To send bitcoin, the following are needed:
- Bitcoin Address of the Recipient: This is a string of alphanumeric characters that uniquely identifies the recipient’s wallet.
- Sufficient Bitcoin Balance: Ensure that there is enough bitcoin to cover the amount to be sent and any associated transaction fees.
- Access to the Wallet: Whether it’s a hardware, software, or web wallet, access to it is required to initiate the transaction.
The Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Access the Wallet
Open the Bitcoin wallet. For a hardware wallet, connect it to a computer and enter the PIN. For software and web wallets, simply log in or open the app.
Step 2: Navigate to the Send Bitcoin Section
Most wallets have a straightforward interface. Look for a section labeled “Send Bitcoin,” “Send,” or something similar. Click on it to proceed.
Step 3: Enter the Recipient’s Bitcoin Address
Copy the recipient’s Bitcoin address and paste it into the designated field or scan the QR code. Double-check the address to ensure it’s correct. Sending bitcoin to the wrong address can result in a permanent loss of funds, as Bitcoin transactions are irreversible.
Step 4: Specify the Amount
Enter the amount of bitcoin to be sent. Most wallets allow users to enter the amount in bitcoin (BTC) or their local currency, with a conversion rate provided.
Step 5: Adjust Transaction Fees
Bitcoin transactions involve fees paid to miners for processing and confirming the transaction. Some wallets allow users to adjust the fee. Higher fees can result in faster confirmation times, while lower fees delay the transaction. Balance the need for speed with cost.
Step 6: Review and Confirm
Before sending, review all details carefully:
- Recipient’s Bitcoin address
- Amount of bitcoin
- Transaction fee
Once confident that everything is correct, confirm the transaction. This may involve entering a password or PIN or pressing a button on the hardware wallet.
Step 7: Transaction Confirmation
After initiating the transaction, a confirmation screen with a transaction ID will appear. This ID allows users to track the status of their transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Transferring from one hardware wallet to another? This video shared by Bitcoin University could be useful:
Sending Bitcoin using the CashApp wallet (a centralized exchange) demonstrates how easy it is to transfer bitcoin to any other wallet, whether it’s a cold wallet or a hot wallet.
Monitoring the Transaction
Bitcoin transactions go through several stages of confirmation on the blockchain. Here’s a brief overview:
- Broadcast: The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network.
- Unconfirmed: Miners see the transaction but still need to include it in a block.
- Confirmed: Once included in a block, the transaction receives its first confirmation. Multiple confirmations (typically six) are considered very secure.
Blockchain explorers like Blockchair or Mempool.space can be used to monitor the transaction status using the transaction ID.
A more in-depth video covering the entire process from sending to receiving, is shared by 99Bitcoins:
Tips for a Smooth Transaction
- Double-Check Addresses: Always verify the recipient’s address to avoid mistakes.
- Use QR Codes: If available, use QR codes to scan addresses directly from the device to minimize errors.
- Beware of Phishing: Ensure that legitimate wallet software and websites are used. Phishing attacks can trick users into sending bitcoin to fraudulent addresses.
- Keep the Wallet Secure: Regularly update wallet software and use strong passwords. For hardware wallets, keep the recovery seed phrase secure and offline.
Conclusion
Sending bitcoin is a straightforward process once the basics are understood. By following the steps outlined in this guide, users can confidently send bitcoin to another wallet, whether it’s to pay for goods, services, or simply transfer funds to another person.
Bitcoin is more than just a digital currency; it’s a movement towards financial freedom and decentralization. Embrace it, use it wisely, and contribute to the growing Bitcoin ecosystem.










