Table of Contents
Redefining Scarcity in the Digital Age
Bitcoin is more than a financial innovation; it’s a revolutionary redefinition of digital scarcity in the modern era. Traditional scarcity is defined by the economic principle where limited resources contrast with seemingly unlimited human wants, influencing the perceived value of an asset. Bitcoin, as the first decentralized digital currency, introduces the concept of digital scarcity, a novel phenomenon made possible and meaningful through its unique blend of technological and economic properties.
Bitcoin: The First Decentralized Digital Currency
Bitcoin stands apart as the first of its kind: a decentralized digital currency that operates independently of any central authority. It transcends the limitations of physical borders and traditional banking systems, representing a new form of asset that is not just digital but also finite in nature. This characteristic of finiteness is crucial to understanding Bitcoin’s value proposition in the broader context of currencies and assets.
The Mining Process: Establishing Digital Scarcity
The heart of Bitcoin’s network lies in mining, a process that is critical to maintaining its ecosystem. Mining involves validators, known as miners, who use powerful computers to secure the network and process transactions. In return, they are rewarded with new bitcoin.
This process is resource-intensive and deliberately designed to mimic the physical mining of resources like gold, underscoring the concept of scarcity in the digital realm. The comparison to gold is apt, as both resources are finite and require significant effort to extract, which in turn reinforces their value.

The Immutable Laws of Bitcoin’s Code
At the core of Bitcoin’s design are two immutable laws that govern its scarcity:
The Supply Cap: Limiting Bitcoin to 21 Million
Bitcoin’s total supply is hard-capped at 21 million coins. This cap is crucial as it contrasts sharply with the endless printing capabilities of fiat currencies, which are prone to inflation and devaluation. This finite supply echoes the scarcity of precious metals and is a fundamental reason for Bitcoin’s comparison to digital gold.
Bitcoin Controlled Supply Chart
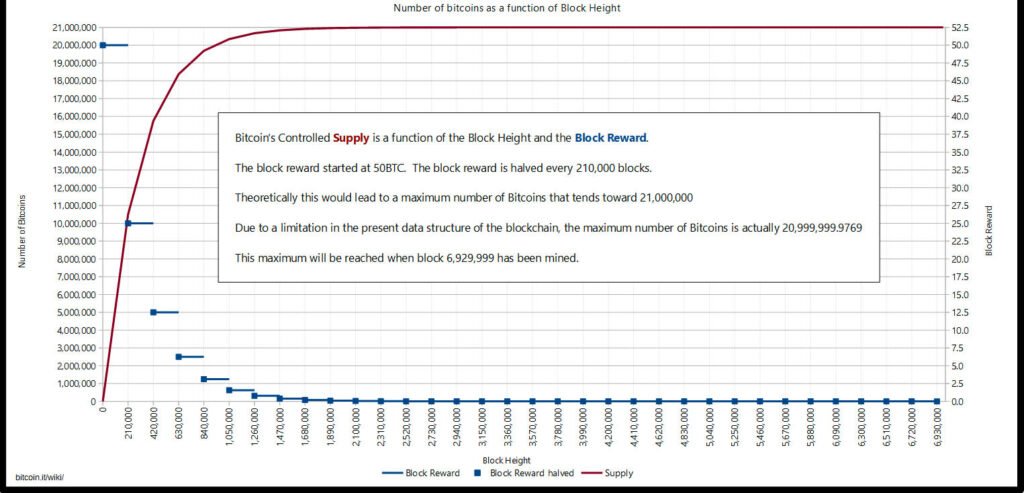
The Controlled Emission Rate: The Halving Events
Every four years, the Bitcoin network undergoes a “halving” event, where the reward for mining new blocks is halved. This mechanism mimics the diminishing returns of gold mining and is pivotal in reducing the flow of new bitcoin into the market, thus enhancing its scarcity.
Bitcoin Halving Schedule Fibonacci Spiral

The Economics of Scarcity: Understanding Bitcoin’s Value
Scarcity is a key driver of value in economics. The limited nature of resources in contrast to human desire and need creates a natural valuation of assets. Bitcoin embodies this principle by limiting its supply, thereby making each unit inherently more valuable as the total cap is approached. This economic principle helps demystify why Bitcoin holds value and continues to attract investment.
Historical Context: Scarcity Through the Ages
Throughout history, the value of assets like gold, diamonds, and rare artworks has been significantly influenced by their scarcity. Bitcoin fits into this historical narrative as a digital asset whose value is derived in part from its limited availability, much like these traditional scarce resources.
Halving Events: Countdown to Ultimate Scarcity
The halving events are not merely technical occurrences; they are fundamental to the economic structure of Bitcoin. Each halving, which occurs every 210,000 blocks or roughly every 4 years, reduces the rate at which new bitcoin are created, thus slowly marching the currency towards its ultimate cap of 21 million. These events are akin to a countdown, with each step heightening the scarcity and potentially increasing the value of bitcoin.

Contrast with Fiat and Altcoins: The Scarcity Differential
In stark contrast to fiat currencies, which are subject to inflation and government control, Bitcoin offers a deflationary alternative. Furthermore, most alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) lack Bitcoin’s stringent supply controls, making them more susceptible to devaluation and centralization.

Demand and Scarcity: A Symbiotic Relationship
Bitcoin’s scarcity is significantly amplified by its increasing demand. Factors like its growing acceptance as a store of value, its reputation as digital gold, and the burgeoning interest from both retail and institutional investors drive this demand. This relationship between scarcity and demand creates a powerful economic and psychological appeal.
Lost Coins: An Unintended Boost to Scarcity
A unique aspect contributing to Bitcoin’s scarcity is the phenomenon of lost coins. Over the years, a significant number of bitcoin have been lost due to various reasons, such as forgotten private keys, hard drive failures, or users passing away without leaving access to their Bitcoin wallets.
These lost coins effectively reduce the circulating supply of Bitcoin, further accentuating its scarcity. Unlike traditional assets, these lost digital coins are irretrievable, making each remaining bitcoin even more scarce and potentially more valuable. In 2020, Chainalysis estimated that 3.7 million bitcoin have been lost.

The Psychological Impact of Scarcity
The concept of scarcity has a profound psychological effect on human behavior. The desire to own something rare and valuable is deeply ingrained in human psychology. Bitcoin’s finite nature taps into this desire, creating a strong appeal and demand that extends beyond its economic principles.
Consensus: The Guardian of Bitcoin’s Rules
The Bitcoin network operates on a consensus mechanism, which ensures that its foundational rules, such as the 21 million supply cap, are upheld by the majority of its participants. This consensus model adds a layer of democratic governance to Bitcoin, making any change to these fundamental aspects exceedingly challenging.
Mining Difficulty and Network Security: Safeguarding Scarcity
As Bitcoin evolves, the mining process becomes more challenging, requiring more computing power. This increasing difficulty ensures the security of the network and the integrity of Bitcoin’s scarcity. This dynamic adjustment of mining difficulty is crucial in maintaining consistent block times and the overall security of the Bitcoin network.

Bitcoin and Blockchain: The Value of Proof-of-Work
While blockchain technology is groundbreaking, it’s important to note that its value is fully realized in the context of Bitcoin’s proof-of-work system. This system underpins the security and functionality of Bitcoin’s blockchain, setting it apart from other blockchain implementations that lack the same level of decentralization and security.
Scarcity and Network Effects: A Feedback Loop
Bitcoin’s scarcity is closely tied to its network effects. As more people adopt and invest in Bitcoin, its limited supply becomes more pronounced, leading to increased demand and potentially higher prices. This feedback loop between scarcity and network effects is a critical component of Bitcoin’s economic model.
Conclusion: The Multifaceted Nature of Bitcoin’s Scarcity
Bitcoin’s scarcity is not a mere technical feature; it is a fundamental aspect that emerges from a confluence of technological innovation, economic principles, psychological factors, and network effects. This multifaceted nature of scarcity redefines the concept of value in the digital era, positioning Bitcoin as more than a currency – it is a finite digital resource that offers a new perspective on scarcity and value in our increasingly digital world.
FAQ
What is Bitcoin’s significance?
Bitcoin represents a revolutionary redefinition of digital scarcity by combining technological and economic properties, introducing a finite and decentralized digital currency.
u003cstrongu003eHow does Bitcoin differ from traditional currencies?u003c/strongu003e
Unlike fiat currencies prone to inflation, Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million coins, making it inherently scarce and comparable to precious metals like gold.
u003cstrongu003eWhat role does the mining process play in establishing digital scarcity for Bitcoin?u003c/strongu003e
Mining, a resource-intensive process mimicking physical mining, is crucial in securing the network and processing transactions, thereby contributing to Bitcoin’s digital scarcity.
u003cstrongu003eWhat laws govern Bitcoin’s scarcity?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin’s scarcity is governed by the supply cap of 21 million coins and the controlled emission rate through halving events every four years, reducing the rate of new bitcoin creation.
Why is Bitcoin’s scarcity important?
Scarcity, a key driver of value in economics, is embodied by Bitcoin’s limited supply, creating a natural valuation of its units as the total cap is approached.
u003cstrongu003eHow do halving events contribute to Bitcoin’s ultimate scarcity?u003c/strongu003e
Halving events, occurring every 210,000 blocks, reduce the rate of new bitcoin creation, incrementally heightening scarcity and potentially increasing Bitcoin’s value.
u003cstrongu003eHow does Bitcoin’s scarcity compare to fiat currencies and alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins)?u003c/strongu003e
Bitcoin offers a deflationary alternative to fiat currencies and stands out from altcoins due to its stringent supply controls, contrasting with the inflationary nature of fiat and altcoins.
u003cstrongu003eHow does demand interact with Bitcoin’s scarcity to influence its value?u003c/strongu003e
Increasing demand, driven by factors like acceptance as a store of value and institutional interest, amplifies Bitcoin’s scarcity, creating a powerful economic and psychological appeal.
u003cstrongu003eWhat is the impact of lost coins on Bitcoin?u003c/strongu003e
Lost coins, irretrievable due to various reasons, reduce the circulating supply, accentuating Bitcoin’s scarcity. An estimated 3.7 million bitcoins were lost by 2020.
u003cstrongu003eHow does consensus and the proof-of-work system contribute to safeguarding Bitcoin’s scarcity?u003c/strongu003e
Consensus ensures adherence to fundamental rules, and the proof-of-work system, integral to Bitcoin’s blockchain, enhances security, safeguarding the integrity of Bitcoin’s scarcity.










