Once a person understands the basic steps of Bitcoin, sending or receiving it is as straightforward as using any digital payment service. This guide breaks down how to make a first Bitcoin transaction in a simple, beginner-friendly way, ensuring the first experience is seamless and secure.
Setting Up a Bitcoin Wallet
Before making any Bitcoin transaction, one needs a Bitcoin wallet to send or receive funds. A Bitcoin wallet is a software or hardware tool that stores the private keys necessary to access and manage bitcoin.
There are several different types of Bitcoin wallets:
- Software Wallets: These are apps that can be downloaded on a phone or computer. Popular options include Sparrow or BlueWallet. Software wallets are ideal for quick access to the Bitcoin network.
- Hardware Wallets: These are physical devices, such as Coldcard or Bitkey, that store private keys offline. They are more secure than software wallets but require additional steps to set up.
- Web Wallets: These are custodial or exchange wallets that are accessible through web interface.
Setting up a Bitcoin wallet is easy:
- Download the Wallet: Choose a software or mobile wallet and download it from the official website or app store. For hardware wallets, purchase the device from a trusted manufacturer’s main website.
In case of web wallets, you need to sign up on the provider’s website or exchange, and possibly complete KYC procedures. - Create a New Wallet: Open the wallet app and follow the instructions to create a new Bitcoin wallet. This typically involves generating a recovery seed for non-custodial wallets—a series of words that act as a backup to recover bitcoin in case the device is lost or damaged.
- Back-Up the Recovery Phrase: Write down the recovery phrase on paper or a etch them on a steel plate and store it in a secure place. Never share this phrase with anyone, as it provides full access to the Bitcoin private keys stored in the wallet.
Receiving Bitcoin
Once the wallet is set up, the next step is to receive bitcoin. This could come from buying bitcoin on an exchange, receiving it from a friend, or receiving it as payment for goods or services.
- Get the Wallet Address: Open the wallet app and find the “Receive” option. This will generate a unique Bitcoin address—a long string of letters and numbers. Some wallets also provide a QR code for easier scanning.
- Share the Bitcoin Address: Provide this address to the person or service sending bitcoin. Double-check the address to ensure accuracy, as Bitcoin transactions are irreversible.
- Wait for the Transaction to Confirm: Once the bitcoin is sent to the address, it will take some time for the transaction to be confirmed on the Bitcoin network.
Initial confirmations may take about 10 minutes, but more confirmations are needed to finalize the transaction fully. Most wallets show the transaction status and notify users when it is confirmed.
Sending Bitcoin
After receiving bitcoin, a person may want to send it to another wallet, pay for services, or make a purchase. Sending bitcoin is easy once the wallet is funded.
- Obtain the Recipient’s Bitcoin Address: Ask the recipient for their Bitcoin address, just as one would provide theirs when receiving bitcoin.
- Open the Wallet App: In the app, locate the “Send” option. Enter the recipient’s Bitcoin address in the designated field. Many wallets allow scanning a QR code to avoid manual entry and reduce errors.
- Enter the Amount to Send: Specify how much bitcoin to send. Bitcoin wallets allow sending bitcoin in small fractions (also called satoshis), so there’s no need to send a whole bitcoin. For example, someone can send 10,000 satoshis (0.0001 BTC) or even less.
- Adjust Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions require network fees to be processed by miners. Some wallets like Sparrow, allow adjusting these fees manually:
- Low fees: These may result in slower confirmations, especially during times of network congestion.
- High fees: These prioritize the transaction, confirming it faster but at a higher cost.
- Approving the Transaction: Review all the details—recipient address, amount, and fee—before approving. Bitcoin transactions cannot be undone once broadcast to the network, so accuracy is crucial.
- Send and Wait for Confirmation: After approving the transaction, the transaction will be broadcast to the network. Like receiving bitcoin, this can take several minutes for the first confirmation, with more confirmations providing greater security.
Verifying the Transaction
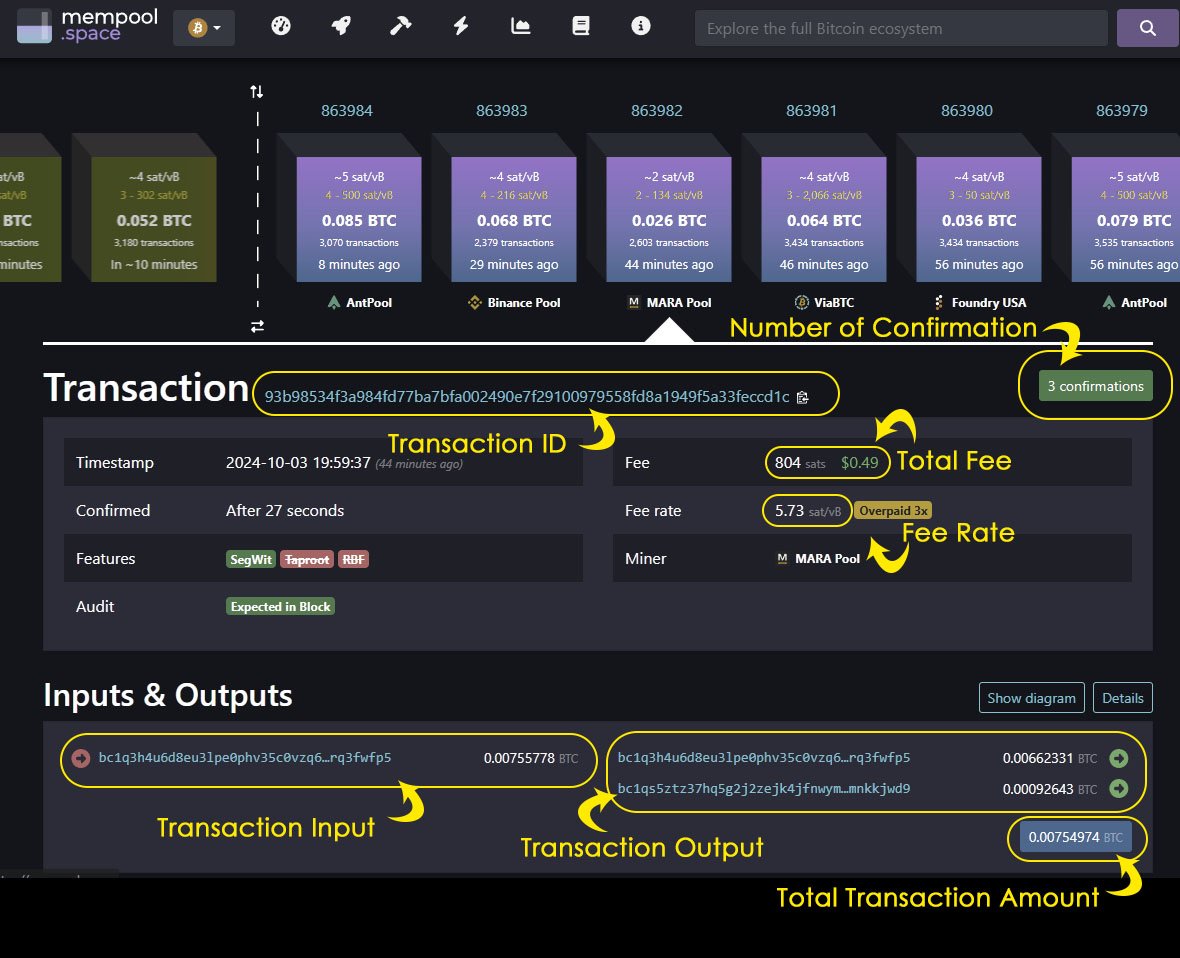
Each Bitcoin transaction is publicly recorded on the blockchain, a decentralized ledger. It’s possible to verify a transaction using a block explorer, a tool that shows the transaction’s status.
- Copy the Transaction ID (TXID): After sending or receiving bitcoin, the wallet app will typically provide a transaction ID. Copy this ID.
- Use a Block Explorer: Visit a block explorer like blockchain.com or mempool.space and paste the transaction ID into the search bar. This will display details about the transaction, including the number of confirmations and the total amount sent.
Security Tips for Your First Bitcoin Transaction
When making a Bitcoin transaction for the first time, it’s essential to prioritize security:
- Double-check Addresses: Always verify that the Bitcoin address is correct before sending funds. Copy-paste errors or malwares replacing the address could cause problems, so being cautious is vital.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Protect the wallet with a strong password and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where available.
- Beware of Scams: Be cautious of phishing attempts, fake wallets, or websites pretending to be legitimate Bitcoin services.
Conclusion
Making a Bitcoin transaction for the first time is a straightforward process once the basic steps are understood.
By setting up a secure Bitcoin wallet, receiving bitcoin, and sending it while ensuring accuracy, anyone can confidently navigate their first transaction.
With a little practice and attention to detail, Bitcoin transactions will become as second nature as using any other payment method.










