For months, the specter of “recession 2023” loomed large, casting a shadow over household budgets and business plans. The December Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting emerged as a pivotal moment. Following a period of unprecedentedly rapid rate hikes, the Federal Reserve provided a semblance of optimism by maintaining the federal funds rate at 5.25% – 5.50%.
The markets interpreted this as an indication of a more measured shift away from the previously aggressive rate increases. This stance, in conjunction with the recent trends of decreasing inflation and a slowdown in economic growth, points to a possible alleviation of the looming recession concerns.

Recession 2023: Interpreting the Fed’s Role From An Austrian Perspective
The Austrian economics lens casts a critical eye on the Federal Reserve’s efforts to manage inflation.
This school of thought likens the Fed, charged with currency and interest rate oversight, to an “arsonist” attempting to extinguish a fire it has kindled. The contradiction lies in entrusting an entity that actively engages in monetary expansion and interest rate manipulation with the task of curbing inflation.
Austrian economists also critique the dependence on government-regulated monetary systems, predominantly debt-fueled, which fundamentally conflict with the original role of money as a means to liquidate debts. This perspective underscores the deep-seated issues inherent in expecting effective inflation control from an institution fundamentally at odds with such objectives.
Is Bitcoin A Hedge Against Inflation?
Discussing inflation inevitably brings Bitcoin into focus, especially from an Austrian viewpoint.
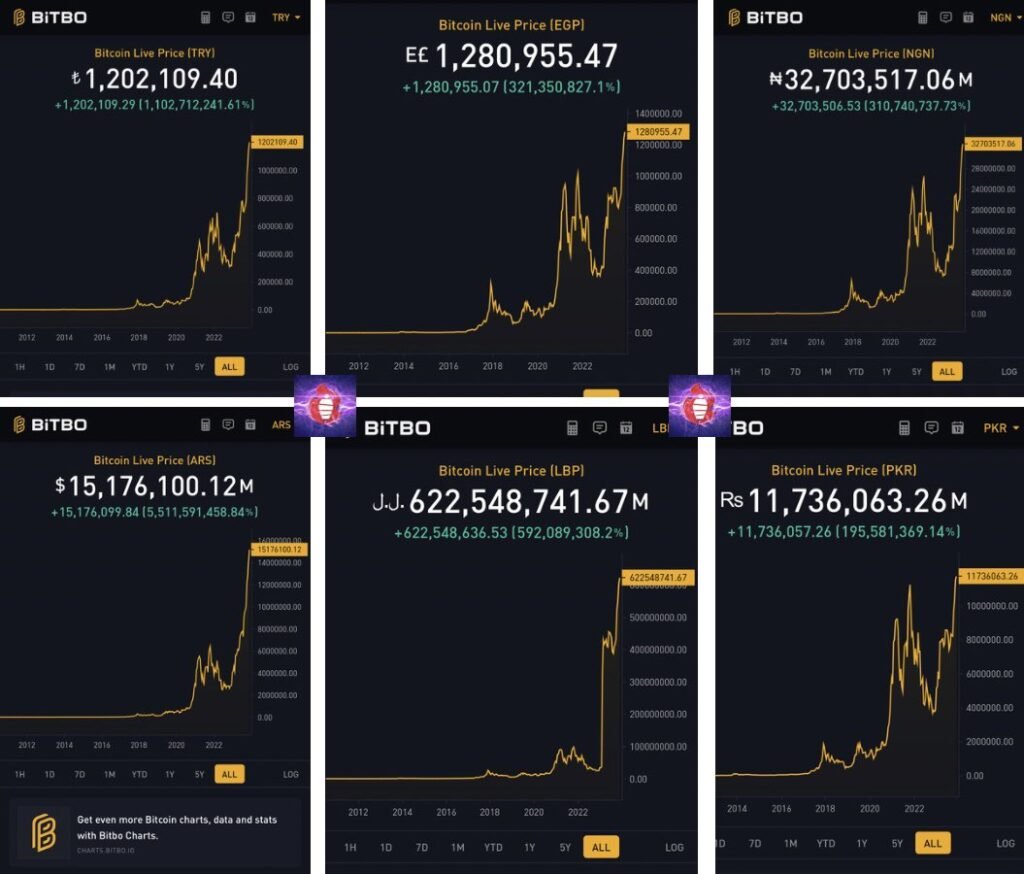
Bitcoin stands out as a robust alternative to conventional fiat currencies, owing to its decentralized framework and finite supply. This unique structure inherently protects it against inflation. In stark contrast to fiat currencies, which are subject to unlimited printing by central banks, Bitcoin’s supply is capped, effectively safeguarding its value from dilution by excessive issuance.
This characteristic positions Bitcoin not just as a digital asset but as a compelling hedge against the inflationary tendencies of traditional monetary systems. Its volatility when measured in fiat terms is a testament to its existence as one of the few truly free markets, unshackled by centralized control.
The Business Cycle and Federal Reserve Interventions
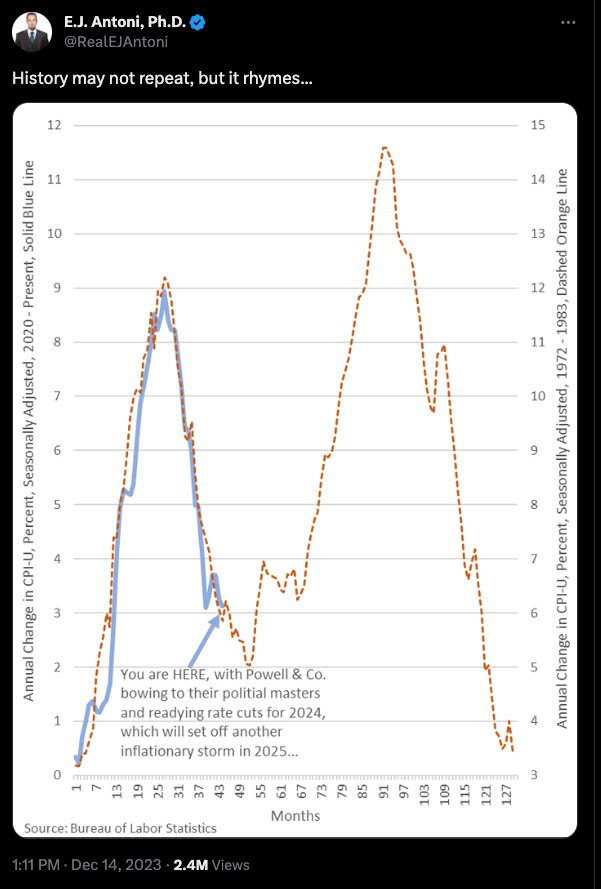
Austrian economists interpret the business cycle as primarily a product of, if not entirely induced by, Central Bank interventions, like the Federal Reserve. These activities, especially the manipulation of interest rates, are seen as catalysts for artificial economic booms and subsequent busts.
This viewpoint posits that such tampering leads to misallocated investments during boom phases followed by unavoidable corrections or recessions. This casts doubt on the effectiveness of Central Bank strategies in achieving economic stability. Many believe these interventions actually exacerbate the very economic fluctuations they aim to smooth out.
Conclusion: A Question of Economic Stability
In the shadow of the 2023 recession, there’s growing skepticism about the reliability of government-reported economic figures, with anecdotal evidence painting a grim picture of rampant inflation and widespread financial distress.
This climate casts doubt on the narrative of a “soft landing” and economic recovery. While there’s some relief at the Federal Reserve’s cautious approach to rate hikes, the underlying issues rooted in the post-2020 massive monetary expansion loom large.
The situation underscores the urgent need for a paradigm shift. The current economic stabilization attempts, though well-intentioned, might be insufficient in addressing the systemic flaws exposed by this crisis. This is why Bitcoiners advocate for a departure from conventional, interventionist monetary policies and suggest a pivot towards a more market-oriented, deflationary monetary system.
Bitcoin’s inherent deflationary nature, in stark contrast to the inflationary tendencies of traditional fiat currencies, offers a compelling argument for its adoption. As the world grapples with the aftermath of unrestrained money printing and its inflationary consequences, the appeal of a decentralized, deflationary monetary system becomes increasingly evident. This shift could mark a pivotal step towards genuine economic stability and resilience.










