In a recent report shared by CoinShares’ Head of Research, James Butterfill, the digital asset investments manager delves into the potential ramifications of the next Bitcoin halving event, slated for April 2024. The report focuses on the impact on hash rate, miners’ cost structures, and the overall sustainability of the mining network.
Effects of Next Bitcoin Halving on Hash Rate
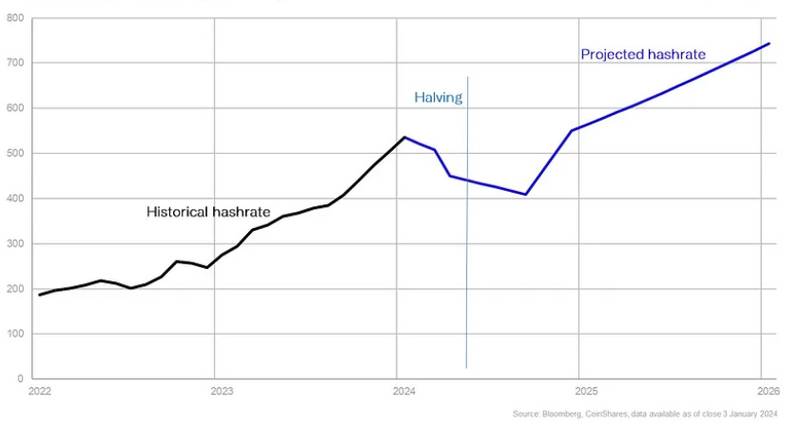
The report highlights the remarkable growth in the Bitcoin mining network, experiencing a staggering 104% increase in hash rate in 2023. As per the historical data, CoinShares expects that by the April 2024 halving, the hashrate will normalize back to the trend line at around 450 EH/s. It further states:
“[Hash rate] could potentially decrease further to 410 EH/s six months later. Following that, the trend line forecasts a sharp increase in the hashrate to approximately 550 EH/s by the end of 2024.”
One of the key findings by CoinShares is the projection of the average cost of production per bitcoin post-halving. While the weighted average cost of production and cash cost stood at around $16,800 and $25,000 per bitcoin for Q3 2023, the company expects both to increase to $27,900 and $37,856, respectively.
The methodology employed in the report involves a meticulous financial analysis for Q3 2023, focusing on 14 miners, 13 of which are publicly listed entities, representing a substantial portion of Bitcoin mining hashpower.
Bitcoin Miner Efficiency
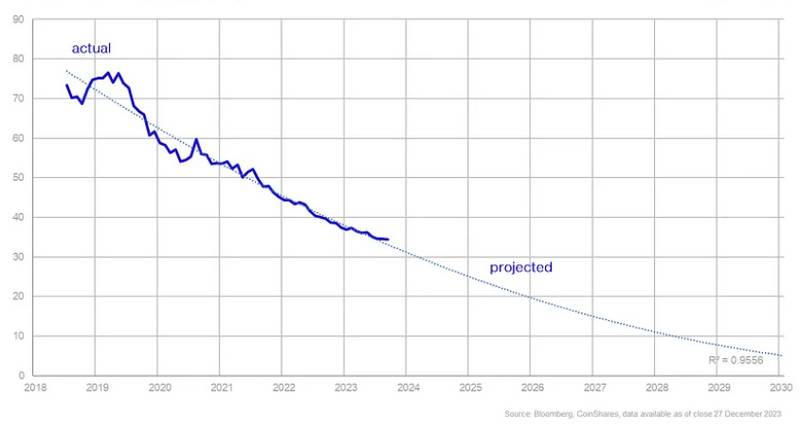
At present, the network maintains a weighted average efficiency of 34 W/TH. In the current year alone, there has been an 8% uptick in efficiency, and spanning the past three years, there has been an overall improvement of 28%.
Extrapolating from these trends, the report anticipates that by mid-2026, the efficiency level could potentially plummet to as low as 10 W/TH. This projection is grounded in the ongoing advancements in chip design and the integration of more efficient mining hardware into the network.
Related reading: Bitmain Unveils The New Antminer S21 Series
Related reading: Auradine Unveils New Teraflux Miner With 375 TH/s Capacity
Challenges for Bitcoin Miners
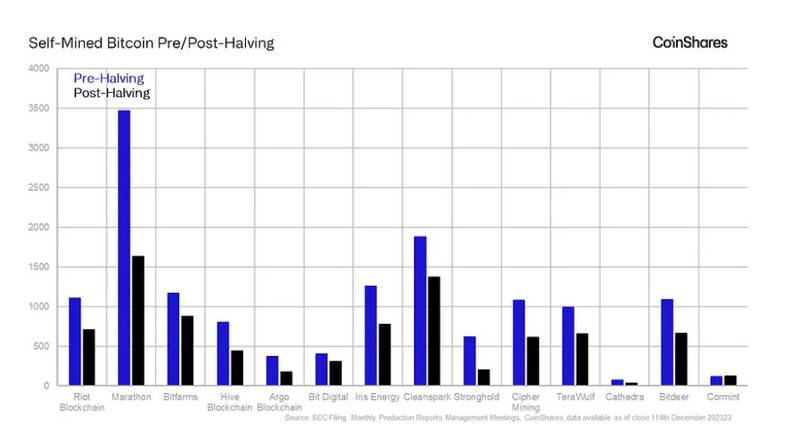
The report outlines the intricate relationship between miners’ computing power, bitcoin production, and the cost structure. It highlights the challenges miners face in maintaining pre-halving bitcoin output by stating:
“For miners to achieve their same pre-halving bitcoin output, they would need to double their market share, which is incredibly challenging given the network hashrate growth of ~53% CAGR over the last three years, or growth in the amount of fees collected per block would need to fully make up for the reduction in the block subsidy caused by the halving.”
Miners’ Cost Dynamics
In the sphere of Bitcoin mining, miners’ cost dynamics hinge on two crucial factors: energy and equipment. According to the report, the publicly monitored miners showcase an average energy consumption of 4.5 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Procuring this energy involves engaging with wholesale markets such as spot or futures markets or entering negotiations with energy providers through Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) contracts.
Despite the collective endeavor to enhance fleet-wide efficiency, the miners are not making improvements in the direct cost structure. CoinShares notes the intrinsic need for miners to heighten their power draw and energy consumption to maintain a consistent bitcoin output.
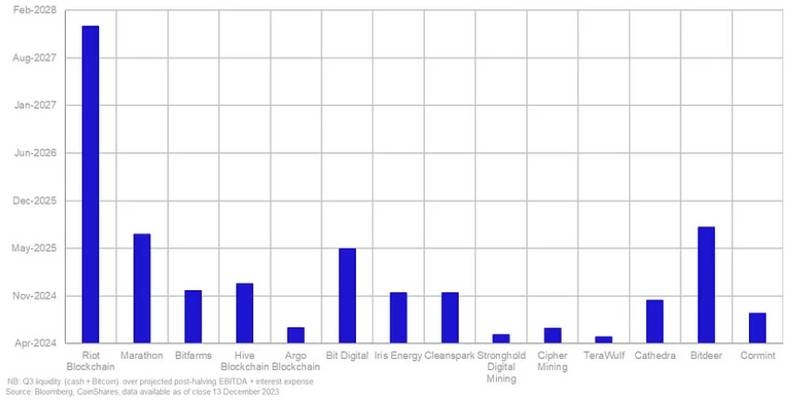
Miner Runway
The report uses a metric called “miner runway”. It’s defined as the duration miners can survive paying off their operational expenditures using their cash and bitcoin reserves.
CoinShares identifies well-capitalized miners with larger bitcoin balances, such as Riot, as better positioned for a sustained bull market. However, miners with a low runway and high cash-cost per bitcoin, like Stronghold, could face challenges in a low bitcoin price environment post-halving.
CoinShares’ report sheds light on the intricate dynamics and challenges faced by Bitcoin miners in the wake of the upcoming halving event. The findings underscore the need for strategic cost management and operational efficiency as the industry braces for a significant shift.










