The concept of a Bitcoin mining farm has emerged as a critical component of the Bitcoin network. These facilities, sometimes sprawling across vast warehouses or even entire industrial complexes, are the backbone of Bitcoin’s decentralized system.
They validate transactions, secure the network, and ensure that the principles set forth by Satoshi Nakamoto remain intact. This article delves into the intricacies of Bitcoin farms, and their role in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
What is a Bitcoin Farm?
A Bitcoin farm, at its core, is a collection of specialized computers designed solely for mining Bitcoin. These farms range from small operations run by enthusiasts in their garages to massive industrial-scale operations that consume megawatts of electricity.
Regardless of size, the fundamental purpose of a Bitcoin mining farm is the same: to participate in the Bitcoin network by solving mathematical equations, thereby validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain.
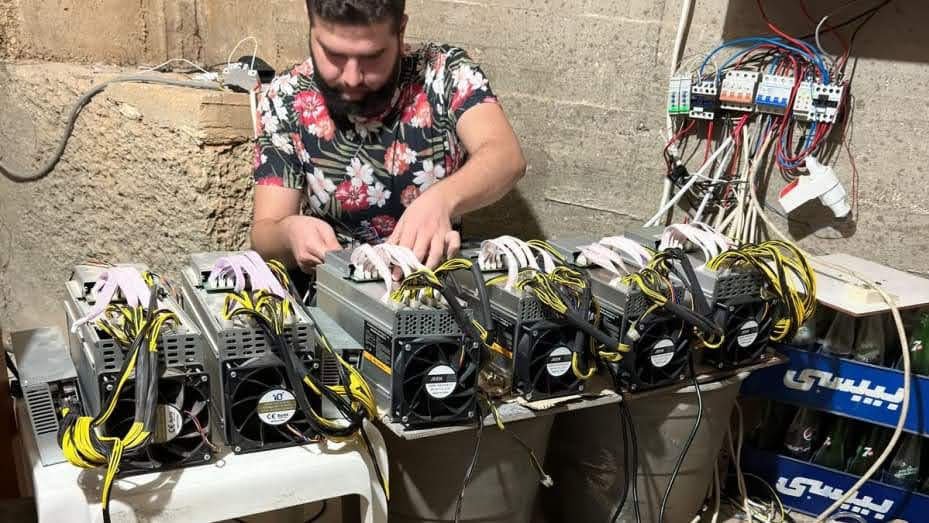

The term “mining” is often used metaphorically, likening the process to the extraction of precious metals like gold. However, instead of physical digging, Bitcoin mining involves computational work.
The computers, known as miners, race to solve a mathematical problem. The first to solve the problem gets the privilege of adding a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoin.
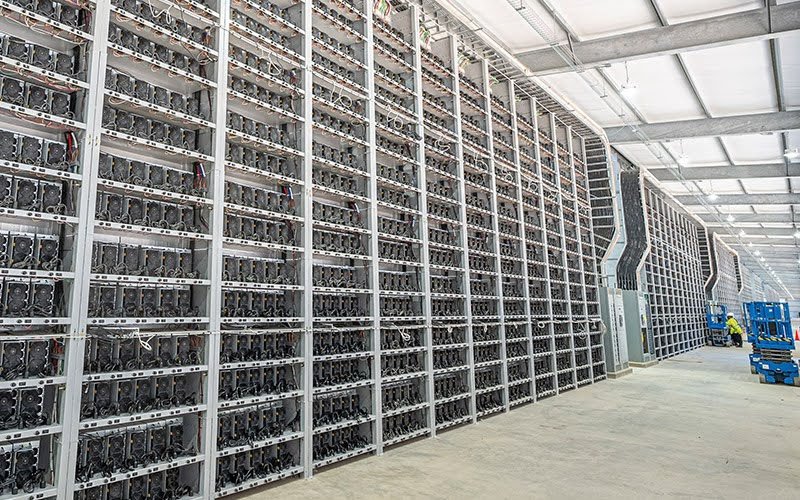

The Hardware Behind the Magic
The heart of any Bitcoin mining farm lies in its hardware. Unlike traditional computing, where general-purpose CPUs or GPUs might suffice, Bitcoin mining requires specialized equipment known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits).
These devices are engineered exclusively for the task of mining Bitcoin, offering unparalleled efficiency and power.
ASIC miners are designed to perform one specific function—calculating the SHA-256 hash function, which is integral to the Bitcoin protocol. Their purpose-built nature means they can perform this task much faster and with significantly less energy than a standard computer.
The result is a competitive environment where the success of a Bitcoin farm depends heavily on the quality and quantity of ASIC miners deployed, and electricity cost.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability
One of the most discussed aspects of Bitcoin farms is their energy consumption.
Mining Bitcoin is an energy-intensive process, and large-scale Bitcoin farms can consume as much electricity as small towns. This has led to criticism from various quarters, primarily from those concerned about environmental impact.
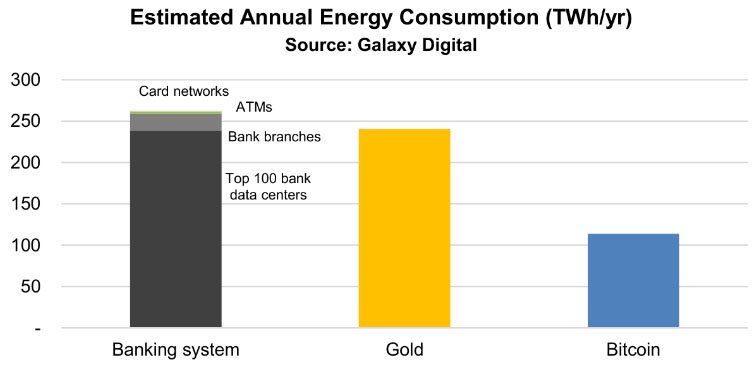
However, it’s essential to consider the bigger picture. The energy used by Bitcoin farms is not wasted; it secures the most decentralized and transparent monetary system ever created.
Moreover, many Bitcoin farms are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources. Hydroelectric power, wind farms, and solar energy are becoming more common in the Bitcoin mining industry.
This shift towards green energy not only addresses environmental concerns but also makes economic sense, as renewable energy can be more cost-effective in the long run.
Economic Implications of Bitcoin Farms
The rise of Bitcoin farms has far-reaching economic implications.
Firstly, they represent a new and unique industry that provides jobs, stimulates technological innovation, and contributes to local economies. In regions with cheap electricity, Bitcoin farms have become significant economic players.
Secondly, Bitcoin farms play a critical role in the stability and security of the Bitcoin network.
By maintaining the integrity of the blockchain, they ensure that Bitcoin remains a secure and trustworthy store of value, free from the risks associated with traditional financial systems, such as currency devaluation and government interference.
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin means that no single entity controls the network, and Bitcoin farms are the physical manifestation of this decentralization. They are also nodes that validate transactions, making Bitcoin’s promise of a decentralized financial system a reality.
Challenges and Future of Bitcoin Farms
Despite their importance, Bitcoin farms face several challenges.
The increasing difficulty of mining, driven by Bitcoin’s inbuilt deflationary mechanism, means that the computational power required to mine a single bitcoin block is continually rising.
This necessitates constant upgrades to hardware and infrastructure, increasing operational costs.
Regulatory scrutiny is another challenge. Governments around the world are still grappling with how to regulate Bitcoin and, by extension, Bitcoin farms.
In some regions, restrictive regulations have forced miners to relocate to more favorable environments.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable. The relentless pace of technological innovation in the Bitcoin space suggests that more efficient mining technologies and more favorable regulatory environments are on the horizon.
In conclusion, Bitcoin farms are not just industrial complexes filled with whirring machines; they are the engines of a financial revolution. They embody the principles of decentralization, security, and innovation that make Bitcoin unique.










