Warren Buffett, often hailed as one of the most successful investors of all time, has built his reputation and fortune on a keen understanding of traditional market fundamentals.
As the chairman and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway, Buffett has consistently championed value investing, focusing on companies with strong fundamentals, reliable earnings, and competitive advantages.
Warren Buffet’s Bitcoin skepticism contrasts sharply with a decentralized digital currency that has captured the imagination of a new generation of investors.
Buffett’s investment philosophy is rooted in tangible value. He famously avoids sectors and technologies he doesn’t fully understand, which has led him to steer clear of high-tech stocks and speculative ventures.
His investment strategy is epitomized by long-term holdings in companies like Coca-Cola, American Express, and Apple—firms with enduring business models and strong track records of profitability.
This approach has yielded extraordinary results over the decades, cementing Buffett’s legacy as a financial titan.
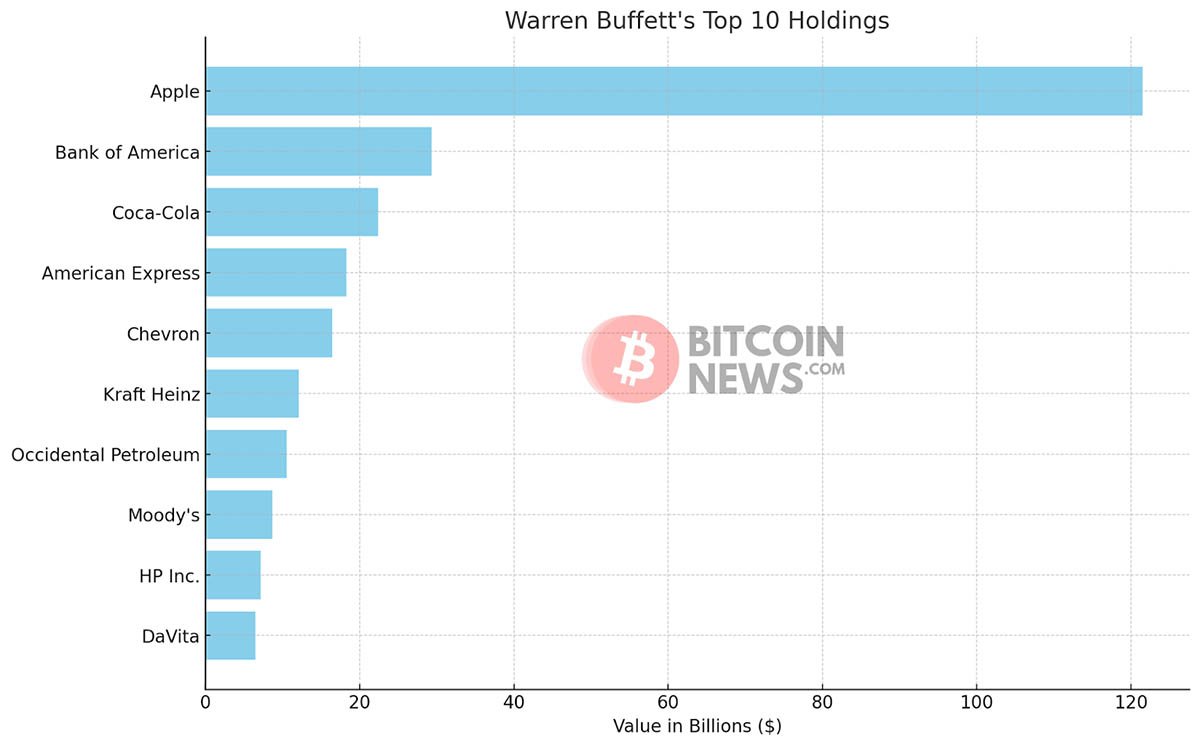
In stark contrast to Buffett’s steady and predictable investment style, Bitcoin represents a new frontier in finance—volatile, unpredictable, and driven by innovative potential.
Launched in 2009 by an anonymous figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin was initially a niche interest among tech enthusiasts and libertarians. However, it has since grown into a global phenomenon, challenging traditional financial systems and offering a glimpse into the future of money.
Buffett’s skepticism towards Bitcoin is well-documented. He has famously described it as “rat poison squared” and dismissed it as a non-productive asset.
From Buffett’s perspective, Bitcoin lacks intrinsic value because it does not generate earnings, pay dividends, or provide any utility that he considers essential for a sound investment.
Instead, its value is derived largely from the belief that someone else will pay more for it in the future—a concept that Buffett associates with the speculative bubbles of the past.
Despite Buffett’s criticism, Bitcoin has attracted a growing base of supporters who argue that it represents a revolutionary form of money.
Proponents claim that Bitcoin’s decentralized nature and limited supply make it an ideal hedge against inflation and a reliable store of value in a world where central banks print money at unprecedented rates.
They also highlight Bitcoin’s potential to provide financial services to the unbanked and to facilitate transactions in a manner that is faster, cheaper, and more secure than traditional banking systems.
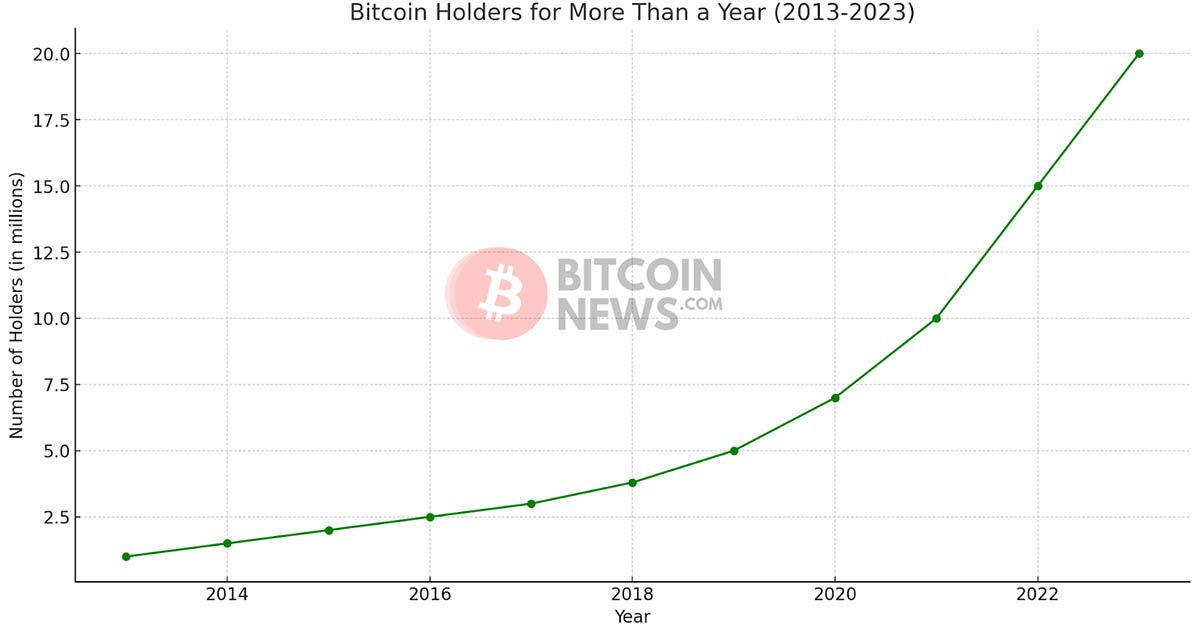
Bitcoin’s ability to offer financial services to the unbanked is particularly significant. In many parts of the world, access to traditional banking services is limited or non-existent.
Bitcoin, with its decentralized and borderless nature, provides a viable alternative for millions of people, enabling them to participate in the global economy.
This aspect of Bitcoin aligns with broader goals of financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
One of the most striking aspects of Bitcoin’s rise is its ability to challenge the status quo. Unlike fiat currencies, which are controlled by central banks and governments, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers.
This feature appeals to those who are wary of centralized power and the potential for government overreach. Additionally, Bitcoin’s pseudonymous nature provides a level of privacy that is increasingly rare in an age of digital surveillance.
While bitcoin’s price volatility is often cited as a drawback, it also reflects the dynamic and rapidly evolving nature of this new asset class.
Related: Why Bitcoin Volatility is a Small Price to Pay
Early adopters and visionaries see this volatility as part of the maturation process, a necessary phase in the journey towards broader acceptance and stability.
Moreover, the increasing integration of Bitcoin into mainstream financial systems suggests a growing recognition of its potential as a legitimate and valuable asset.
The financial world is not static, and perspectives can evolve. Some of Buffett’s most trusted lieutenants, such as Charlie Munger, share his disdain for Bitcoin.
Still, others in the broader financial industry have begun integrating it into their portfolios and services. Major financial institutions now offer bitcoin-related products, and some countries are even exploring its use as legal tender.
Buffett’s cautious stance on Bitcoin may reflect his deep-seated investment principles, but it also underscores the broader challenge of adapting to rapid technological change.
While he continues to rely on time-tested strategies, the market landscape is shifting in ways that are difficult to ignore. Bitcoin’s ascent, despite its volatility and risks, suggests that new forms of value and investment are gaining traction.
In conclusion, Warren Buffett and Bitcoin represent two distinct paradigms in the financial world. Buffett’s investment philosophy is grounded in tangible value and long-term growth, while Bitcoin embodies the promise and potential of innovation.
The tension between these perspectives illustrates the dynamic and evolving nature of finance, where traditional wisdom and cutting-edge technology coexist and compete.
As Bitcoin continues to mature, its role in the financial ecosystem will likely remain a topic of robust debate, with Buffett’s caution serving as a counterbalance to the optimism of its advocates.
The future of finance may well depend on the ability to integrate these diverse approaches, harnessing the strengths of both traditional and innovative financial models.










